Eckert number: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
en>Rememberlands m Math formatting |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Rectangular hyperbola.svg|thumb|The [[reciprocal function]], exhibiting hyperbolic growth.]] | |||
When a quantity grows towards a [[Mathematical singularity|singularity]] under a finite variation (a "[[finite-time singularity]]") it is said to undergo '''hyperbolic growth'''.<ref>See, e.g., Korotayev A., Malkov A., Khaltourina D. [http://cliodynamics.ru/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=124&Itemid=70 '''Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth''']. Moscow: URSS Publishers, 2006. P. 19-20.</ref> More precisely, the [[reciprocal function]] <math>1/x</math> has a [[hyperbola]] as a graph, and has a singularity at 0, meaning that the [[limit of a function|limit]] as <math>x \to 0</math> is infinite: any similar graph is said to exhibit hyperbolic growth. | |||
==Description== | |||
If the output of a function is [[inversely proportional]] to its input, or inversely proportional to the difference from a given value <math>x_0</math>, the function will exhibit hyperbolic growth, with a singularity at <math>x_0</math>. | |||
In the real world hyperbolic growth is created by certain non-linear [[positive feedback]] mechanisms.<ref>See, e.g., [[Alexander V. Markov]], and [[Andrey Korotayev|Andrey V. Korotayev]] (2007). [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B83WC-4N0HJMK-2&_user=1300184&_coverDate=12%2F31%2F2007&_rdoc=6&_fmt=summary&_orig=browse&_srch=doc-info(%23toc%2333783%232007%23999839995%23671853%23FLA%23display%23Volume)&_cdi=33783&_sort=d&_docanchor=&_ct=9&_acct=C000052237&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=1300184&md5=d9c2663e7fbd6a77385d61334953d75d "Phanerozoic marine biodiversity follows a hyperbolic trend". Palaeoworld. Volume 16. Issue 4. Pages 311-318].</ref> | |||
===Comparisons with other growth=== | |||
Like [[exponential growth]] and [[logistic growth]], hyperbolic growth is highly [[Nonlinear system|nonlinear]], but differs in important respects. | |||
These functions can be confused, as exponential growth, hyperbolic growth, and the first half of logistic growth are [[convex function]]s; however their [[asymptotic behavior]] (behavior as input gets large) differs dramatically: | |||
* logistic growth is constrained (has a finite limit, even as time goes to infinity), | |||
* exponential growth grows to infinity as time goes to infinity (but is always finite for finite time), | |||
* hyperbolic growth has a singularity in finite time (grows to infinity at a finite time). | |||
==Applications== | |||
===Population=== | |||
Certain mathematical models suggest that until the early 1970s the [[world population]] underwent hyperbolic growth (see, e.g., [http://urss.ru/cgi-bin/db.pl?cp=&page=Book&id=37484&lang=en&blang=en&list=14 ''Introduction to Social Macrodynamics''] by [[Andrey Korotayev]] ''et al.''). It was also shown that until the 1970s the hyperbolic growth of the world population was accompanied by quadratic-hyperbolic growth of the world [[GDP]], and developed a number of [[mathematical model]]s describing both this phenomenon, and the [[World-system theory|World System]] withdrawal from the blow-up regime observed in the recent decades. The hyperbolic growth of the [[world population]] and quadratic-hyperbolic growth of the world [[GDP]] observed till the 1970s have been correlated by [[Andrey Korotayev]] and his colleagues to a non-linear second order [[positive feedback]] between the demographic growth and technological development, described by a chain of causation: technological growth leads to more [[carrying capacity]] of land for people, which leads to more people, which leads to more inventors, which in turn leads to yet more technological growth, and on and on.<ref>See, e.g., Korotayev A., Malkov A., Khaltourina D. [http://cliodynamics.ru/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=124&Itemid=70 '''Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth''']. Moscow: URSS Publishers, 2006; Korotayev A. V. [http://jwsr.ucr.edu/archive/vol11/number1/pdf/jwsr-v11n1-korotayev.pdf A Compact Macromodel of World System Evolution // Journal of World-Systems Research 11/1 (2005): 79–93.]; for a detailed mathematical analysis of this issue see [http://arxiv.org/abs/1206.0496 A Compact Mathematical Model of the World System Economic and Demographic Growth, 1 CE - 1973 CE].</ref> Other models suggest exponential growth, logistic growth, or other functions. | |||
===Queuing theory=== | |||
Another example of hyperbolic growth can be found in [[queueing theory]]: the average waiting time of randomly arriving customers grows hyperbolically as a function of the average load ratio of the server. The singularity in this case occurs when the average amount of work arriving to the server equals the server's processing capacity. If the processing needs exceed the server's capacity, then there is no well-defined average waiting time, as the queue can grow without bound. A practical implication of this particular example is that for highly loaded queuing systems the average waiting time can be extremely sensitive to the processing capacity. | |||
===Enzyme kinetics=== | |||
A further practical example of hyperbolic growth can be found in [[enzyme kinetics]]. When the rate of reaction (termed velocity) between an [[enzyme]] and [[substrate (biochemistry)|substrate]] is plotted against various concentrations of the substrate, a hyperbolic plot is obtained for many simpler systems. When this happens, the enzyme is said to follow [[Enzyme kinetics#Michaelis.E2.80.93Menten_kinetics|Michaelis-Menten]] kinetics. | |||
==Mathematical example== | |||
The function | |||
:<math>x(t)=\frac{1}{t_c-t}</math> | |||
exhibits hyperbolic growth with a singularity at time <math>t_c</math>: in the [[limit of a function|limit]] as <math>t \to t_c</math>, the function goes to infinity. | |||
More generally, the function | |||
:<math>x(t)=\frac{K}{t_c-t}</math> | |||
exhibits hyperbolic growth, where <math>K</math> is a [[scale factor]]. | |||
Note that this algebraic function can be regarded as analytical solution for the function's differential:<ref>See, e.g., Korotayev A., Malkov A., Khaltourina D. [http://cliodynamics.ru/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=124&Itemid=70 '''Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth''']. Moscow: URSS Publishers, 2006. P. 118-123.</ref> | |||
:<math> \frac{dx}{dt}=\frac{K}{(t_c-t)^2}=\frac{x^2}{K}</math> | |||
This means that with hyperbolic growth the absolute growth rate of the variable x in the moment t is proportional to the square of the value of x in the moment t. | |||
Respectively, the quadratic-hyperbolic function looks as follows: | |||
:<math>x(t)=\frac{K}{(t_c-t)^2}.</math> | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Heinz von Foerster]] | |||
*[[Technological singularity]] | |||
*[[Paradigm shift]] | |||
*[[List of paradigm shifts in science]] | |||
*[[Scientific mythology]] | |||
*[[Social effect of evolutionary theory]] | |||
*[[Deep ecology]] | |||
===Mathematics=== | |||
*[[Mathematical singularity]] | |||
===Growth=== | |||
*[[Exponential growth]] | |||
*[[Logistic growth]] | |||
==References== | |||
*[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B83WC-4N0HJMK-2&_user=1300184&_coverDate=12%2F31%2F2007&_rdoc=6&_fmt=summary&_orig=browse&_srch=doc-info(%23toc%2333783%232007%23999839995%23671853%23FLA%23display%23Volume)&_cdi=33783&_sort=d&_docanchor=&_ct=9&_acct=C000052237&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=1300184&md5=d9c2663e7fbd6a77385d61334953d75d [[Alexander V. Markov]], and Andrey V. Korotayev (2007). "Phanerozoic marine biodiversity follows a hyperbolic trend". Palaeoworld. Volume 16. Issue 4. Pages 311-318]. | |||
*[[Michael Kremer|Kremer, Michael]]. 1993. "Population Growth and Technological Change: One Million B.C. to 1990," The Quarterly Journal of Economics 108(3): 681-716. | |||
* [[Korotayev]] A., Malkov A., [[Khaltourina D.]] 2006. [http://cliodynamics.ru/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=124&Itemid=70 ''Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth.''] Moscow: URSS. ISBN 5-484-00414-4 . | |||
* [[Rein Taagepera]] (1979) People, skills, and resources: An interaction model for world population growth. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 13, 13-30. | |||
==References== | |||
{{reflist}} | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hyperbolic Growth}} | |||
[[Category:Mathematical analysis]] | |||
[[Category:Theories of history]] | |||
[[Category:Special functions]] | |||
[[Category:Differential equations]] | |||
[[Category:Population]] | |||
[[Category:Demography]] | |||
[[Category:Curves]] | |||
[[Category:Population ecology]] | |||
Revision as of 01:08, 25 June 2013
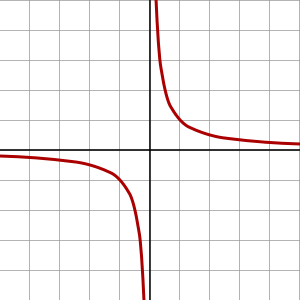
When a quantity grows towards a singularity under a finite variation (a "finite-time singularity") it is said to undergo hyperbolic growth.[1] More precisely, the reciprocal function has a hyperbola as a graph, and has a singularity at 0, meaning that the limit as is infinite: any similar graph is said to exhibit hyperbolic growth.
Description
If the output of a function is inversely proportional to its input, or inversely proportional to the difference from a given value , the function will exhibit hyperbolic growth, with a singularity at .
In the real world hyperbolic growth is created by certain non-linear positive feedback mechanisms.[2]
Comparisons with other growth
Like exponential growth and logistic growth, hyperbolic growth is highly nonlinear, but differs in important respects. These functions can be confused, as exponential growth, hyperbolic growth, and the first half of logistic growth are convex functions; however their asymptotic behavior (behavior as input gets large) differs dramatically:
- logistic growth is constrained (has a finite limit, even as time goes to infinity),
- exponential growth grows to infinity as time goes to infinity (but is always finite for finite time),
- hyperbolic growth has a singularity in finite time (grows to infinity at a finite time).
Applications
Population
Certain mathematical models suggest that until the early 1970s the world population underwent hyperbolic growth (see, e.g., Introduction to Social Macrodynamics by Andrey Korotayev et al.). It was also shown that until the 1970s the hyperbolic growth of the world population was accompanied by quadratic-hyperbolic growth of the world GDP, and developed a number of mathematical models describing both this phenomenon, and the World System withdrawal from the blow-up regime observed in the recent decades. The hyperbolic growth of the world population and quadratic-hyperbolic growth of the world GDP observed till the 1970s have been correlated by Andrey Korotayev and his colleagues to a non-linear second order positive feedback between the demographic growth and technological development, described by a chain of causation: technological growth leads to more carrying capacity of land for people, which leads to more people, which leads to more inventors, which in turn leads to yet more technological growth, and on and on.[3] Other models suggest exponential growth, logistic growth, or other functions.
Queuing theory
Another example of hyperbolic growth can be found in queueing theory: the average waiting time of randomly arriving customers grows hyperbolically as a function of the average load ratio of the server. The singularity in this case occurs when the average amount of work arriving to the server equals the server's processing capacity. If the processing needs exceed the server's capacity, then there is no well-defined average waiting time, as the queue can grow without bound. A practical implication of this particular example is that for highly loaded queuing systems the average waiting time can be extremely sensitive to the processing capacity.
Enzyme kinetics
A further practical example of hyperbolic growth can be found in enzyme kinetics. When the rate of reaction (termed velocity) between an enzyme and substrate is plotted against various concentrations of the substrate, a hyperbolic plot is obtained for many simpler systems. When this happens, the enzyme is said to follow Michaelis-Menten kinetics.
Mathematical example
The function
exhibits hyperbolic growth with a singularity at time : in the limit as , the function goes to infinity.
More generally, the function
exhibits hyperbolic growth, where is a scale factor.
Note that this algebraic function can be regarded as analytical solution for the function's differential:[4]
This means that with hyperbolic growth the absolute growth rate of the variable x in the moment t is proportional to the square of the value of x in the moment t.
Respectively, the quadratic-hyperbolic function looks as follows:
See also
- Heinz von Foerster
- Technological singularity
- Paradigm shift
- List of paradigm shifts in science
- Scientific mythology
- Social effect of evolutionary theory
- Deep ecology
Mathematics
Growth
References
- Alexander V. Markov, and Andrey V. Korotayev (2007). "Phanerozoic marine biodiversity follows a hyperbolic trend". Palaeoworld. Volume 16. Issue 4. Pages 311-318.
- Kremer, Michael. 1993. "Population Growth and Technological Change: One Million B.C. to 1990," The Quarterly Journal of Economics 108(3): 681-716.
- Korotayev A., Malkov A., Khaltourina D. 2006. Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth. Moscow: URSS. ISBN 5-484-00414-4 .
- Rein Taagepera (1979) People, skills, and resources: An interaction model for world population growth. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 13, 13-30.
References
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.
- ↑ See, e.g., Korotayev A., Malkov A., Khaltourina D. Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth. Moscow: URSS Publishers, 2006. P. 19-20.
- ↑ See, e.g., Alexander V. Markov, and Andrey V. Korotayev (2007). "Phanerozoic marine biodiversity follows a hyperbolic trend". Palaeoworld. Volume 16. Issue 4. Pages 311-318.
- ↑ See, e.g., Korotayev A., Malkov A., Khaltourina D. Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth. Moscow: URSS Publishers, 2006; Korotayev A. V. A Compact Macromodel of World System Evolution // Journal of World-Systems Research 11/1 (2005): 79–93.; for a detailed mathematical analysis of this issue see A Compact Mathematical Model of the World System Economic and Demographic Growth, 1 CE - 1973 CE.
- ↑ See, e.g., Korotayev A., Malkov A., Khaltourina D. Introduction to Social Macrodynamics: Compact Macromodels of the World System Growth. Moscow: URSS Publishers, 2006. P. 118-123.









