Ergodic process: Difference between revisions
en>Helpful Pixie Bot m ISBNs (Build KG) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
A '''potentiometer''' is an instrument for measuring the [[Electric potential|potential]] (voltage) in a circuit. Before the introduction of the moving coil and digital volt meters, [[potentiometer]]s were used in measuring [[voltage]], hence the '-meter' part of their name. The method was described by [[Johann Christian Poggendorff]] around 1841 and became a standard laboratory measuring technique.<ref>{{cite web|author=Thomas B. Greenslade, Jr. |url=http://physics.kenyon.edu/EarlyApparatus/Electrical_Measurements/Potentiometer/Potentiometer.html |title=Potentiometer, retrieved 2010 Nov 2 |publisher=Physics.kenyon.edu |date= |accessdate=2013-06-01}}</ref> | |||
In this arrangement, a fraction of a known voltage from a resistive slide wire is compared with an unknown voltage by means of a [[galvanometer]]. The sliding contact or wiper of the potentiometer is adjusted and the galvanometer briefly connected between the sliding contact and the unknown voltage. The deflection of the galvanometer is observed and the sliding tap adjusted until the galvanometer no longer deflects from zero. At that point the galvanometer draws no current from the unknown source, and the magnitude of voltage can be calculated from the position of the sliding contact. | |||
This null balance measuring method is still important in electrical [[metrology]] and standards work and is also used in other areas of electronics. | |||
Measurement potentiometers are divided into four main classes listed below. | |||
== Constant current potentiometer == | |||
[[File:PotenCalibrate2.jpg|left|framed|A potentiometer being calibrated and then measuring an unknown voltage.<br /> R<sub>1</sub> is the resistance of the entire resistance wire. The arrow head represents the moving ''wiper''.]] | |||
In this circuit, the ends of a uniform [[electrical resistance|resistance]] wire R<sub>1</sub> are connected to a regulated [[Direct current|DC]] supply V<sub>S</sub> for use as a voltage divider. The potentiometer is first [[calibration|calibrated]] by positioning the wiper (arrow) at the spot on the R<sub>1</sub> wire that corresponds to the voltage of a standard cell so that <math>{R_2 \over R_1} = {\mbox{cell voltage} \over V_\mathrm{S}}</math> | |||
A standard [[electrochemical cell]] is used whose emf is known (e.g. 1.0183 volts for a [[Weston standard cell]]).<ref>[http://physics.kenyon.edu/EarlyApparatus/Electrical_Measurements/Standard_Cell/Standard_Cell.html Kenyon.edu] Dept of Physics.</ref><ref>[http://www.scenta.co.uk/tcaep/nonxml/science/constant/details/EMF%20of%20Weston%20standard%20cell.htm scenta.co.uk] Scenta.</ref> | |||
The supply voltage V<sub>S</sub> is then adjusted until the [[galvanometer]] shows zero, indicating the voltage on R<sub>2</sub> is equal to the standard cell voltage. | |||
An unknown DC voltage, in series with the galvanometer, is then connected to the sliding wiper, across a variable-length section R<sub>3</sub> of the resistance wire. The wiper is moved until no current flows into or out of the source of unknown voltage, as indicated by the galvanometer in series with the unknown voltage. The voltage across the selected R<sub>3</sub> section of wire is then equal to the unknown voltage. The final step is to calculate the unknown voltage from the fraction of the length of the resistance wire that was connected to the unknown voltage. | |||
The galvanometer does not need to be calibrated, as its only function is to read zero or not zero. When measuring an unknown voltage and the galvanometer reads zero, no current is drawn from the unknown voltage and so the reading is independent of the source's internal resistance, as if by a [[voltmeter]] of [[Infinity|infinite]] resistance. | |||
Because the resistance wire can be made very uniform in cross-section and resistivity, and the position of the wiper can be measured easily, this method can be used to measure unknown DC voltages greater than or less than a calibration voltage produced by a standard cell without drawing any [[Electric current|current]] from the standard cell. | |||
If the potentiometer is attached to a constant voltage DC supply such as a [[lead–acid battery]], then a second variable resistor (not shown) can be used to calibrate the potentiometer by varying the current through the R<sub>1</sub> resistance wire. | |||
If the length of the R<sub>1</sub> resistance wire is AB, where A is the (-) end and B is the (+) end, and the movable wiper is at point X at a distance AX on the R<sub>3</sub> portion of the resistance wire when the galvanometer gives a zero reading for an unknown voltage, the distance AX is measured or read from a preprinted scale next to the resistance wire. The unknown voltage can then be calculated: <math>V_U = V_S {AX \over AB} </math> | |||
== Constant resistance potentiometer == | |||
The constant resistance potentiometer is a variation of the basic idea in which a variable current is fed through a fixed resistor. These are used primarily for measurements in the millivolt and microvolt range. | |||
== Microvolt potentiometer == | |||
This is a form of the constant resistance potentiometer described above but designed to minimize the effects of contact resistance and thermal emf. This equipment is satisfactorily used down to readings of 1000 nV or so. | |||
== Thermocouple potentiometer == | |||
Another development of the standard types was the 'thermocouple potentiometer' especially adapted for temperature measurement with [[thermocouple]]s. | |||
<ref>[http://physics.kenyon.edu/EarlyApparatus/Thermodynamics/Thermocouple_Potentiometer/Thermocouple_Potentiometer.html Kenyon.edu] Dept of Physics. Thermodynamics: Thermocouple Potentiometer.</ref> | |||
Potentiometers for use with thermocouples also measure the temperature at which the thermocouple wires are connected, so that cold-junction compensation may be applied to correct the apparent measured EMF to the standard cold-junction temperature of 0 degrees C. | |||
==Analytical chemistry== | |||
To make a potentiometric determination of an analyte in a solution, the potential of the cell is measured. This measurement must be corrected for the reference and junction potentials. The concentration of the analyte can then be calculated from the [[Nernst Equation]]. Many varieties of this basic principle exist for quantitative measurements. | |||
==Metre bridge== | |||
A metre bridge is a simple type of potentiometer which may be used in school science laboratories to demonstrate the principle of resistance measurement by potentiometric means. A resistance wire is laid along the length of a [[metre rule]] and contact with the wire is made through a [[galvanometer]] by a slider. When the galvanometer reads zero, the ratio between the lengths of wire to the left and right of the slider is equal to the ratio between the values of a known and an unknown resistor in a parallel circuit.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://academia.hixie.ch/bath/wheat/home.html |title=Ian Hickson's Metre Bridge Experiment |publisher=Academia.hixie.ch |date= |accessdate=2013-06-01}}</ref> | |||
== See also == | |||
* [[Potentiometer| Potentiometer (voltage divider)]] | |||
* [[Wheatstone bridge]] | |||
==References== | |||
<references/> | |||
== External links == | |||
* [http://physics.kenyon.edu/EarlyApparatus/Electrical_Measurements/Potentiometer/Potentiometer.html Pictures of measuring potentiometers] | |||
* [http://chem.ch.huji.ac.il/~eugeniik/instruments/test/resistances.htm Electrical calibration equipment including various measurement potentiometers] | |||
{{Electroanalytical}} | |||
[[Category:Voltmeters]] | |||
[[Category:Electrical meters]] | |||
[[Category:Measuring instruments]] | |||
Revision as of 12:23, 19 November 2013
A potentiometer is an instrument for measuring the potential (voltage) in a circuit. Before the introduction of the moving coil and digital volt meters, potentiometers were used in measuring voltage, hence the '-meter' part of their name. The method was described by Johann Christian Poggendorff around 1841 and became a standard laboratory measuring technique.[1]
In this arrangement, a fraction of a known voltage from a resistive slide wire is compared with an unknown voltage by means of a galvanometer. The sliding contact or wiper of the potentiometer is adjusted and the galvanometer briefly connected between the sliding contact and the unknown voltage. The deflection of the galvanometer is observed and the sliding tap adjusted until the galvanometer no longer deflects from zero. At that point the galvanometer draws no current from the unknown source, and the magnitude of voltage can be calculated from the position of the sliding contact.
This null balance measuring method is still important in electrical metrology and standards work and is also used in other areas of electronics.
Measurement potentiometers are divided into four main classes listed below.
Constant current potentiometer
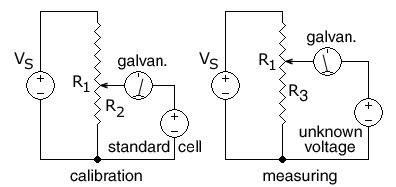
R1 is the resistance of the entire resistance wire. The arrow head represents the moving wiper.
In this circuit, the ends of a uniform resistance wire R1 are connected to a regulated DC supply VS for use as a voltage divider. The potentiometer is first calibrated by positioning the wiper (arrow) at the spot on the R1 wire that corresponds to the voltage of a standard cell so that
A standard electrochemical cell is used whose emf is known (e.g. 1.0183 volts for a Weston standard cell).[2][3]
The supply voltage VS is then adjusted until the galvanometer shows zero, indicating the voltage on R2 is equal to the standard cell voltage.
An unknown DC voltage, in series with the galvanometer, is then connected to the sliding wiper, across a variable-length section R3 of the resistance wire. The wiper is moved until no current flows into or out of the source of unknown voltage, as indicated by the galvanometer in series with the unknown voltage. The voltage across the selected R3 section of wire is then equal to the unknown voltage. The final step is to calculate the unknown voltage from the fraction of the length of the resistance wire that was connected to the unknown voltage.
The galvanometer does not need to be calibrated, as its only function is to read zero or not zero. When measuring an unknown voltage and the galvanometer reads zero, no current is drawn from the unknown voltage and so the reading is independent of the source's internal resistance, as if by a voltmeter of infinite resistance.
Because the resistance wire can be made very uniform in cross-section and resistivity, and the position of the wiper can be measured easily, this method can be used to measure unknown DC voltages greater than or less than a calibration voltage produced by a standard cell without drawing any current from the standard cell.
If the potentiometer is attached to a constant voltage DC supply such as a lead–acid battery, then a second variable resistor (not shown) can be used to calibrate the potentiometer by varying the current through the R1 resistance wire.
If the length of the R1 resistance wire is AB, where A is the (-) end and B is the (+) end, and the movable wiper is at point X at a distance AX on the R3 portion of the resistance wire when the galvanometer gives a zero reading for an unknown voltage, the distance AX is measured or read from a preprinted scale next to the resistance wire. The unknown voltage can then be calculated:
Constant resistance potentiometer
The constant resistance potentiometer is a variation of the basic idea in which a variable current is fed through a fixed resistor. These are used primarily for measurements in the millivolt and microvolt range.
Microvolt potentiometer
This is a form of the constant resistance potentiometer described above but designed to minimize the effects of contact resistance and thermal emf. This equipment is satisfactorily used down to readings of 1000 nV or so.
Thermocouple potentiometer
Another development of the standard types was the 'thermocouple potentiometer' especially adapted for temperature measurement with thermocouples. [4] Potentiometers for use with thermocouples also measure the temperature at which the thermocouple wires are connected, so that cold-junction compensation may be applied to correct the apparent measured EMF to the standard cold-junction temperature of 0 degrees C.
Analytical chemistry
To make a potentiometric determination of an analyte in a solution, the potential of the cell is measured. This measurement must be corrected for the reference and junction potentials. The concentration of the analyte can then be calculated from the Nernst Equation. Many varieties of this basic principle exist for quantitative measurements.
Metre bridge
A metre bridge is a simple type of potentiometer which may be used in school science laboratories to demonstrate the principle of resistance measurement by potentiometric means. A resistance wire is laid along the length of a metre rule and contact with the wire is made through a galvanometer by a slider. When the galvanometer reads zero, the ratio between the lengths of wire to the left and right of the slider is equal to the ratio between the values of a known and an unknown resistor in a parallel circuit.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ Kenyon.edu Dept of Physics.
- ↑ scenta.co.uk Scenta.
- ↑ Kenyon.edu Dept of Physics. Thermodynamics: Thermocouple Potentiometer.
- ↑ Template:Cite web

