Spherical trigonometry: Difference between revisions
en>LGB No edit summary |
en>ChrisGAHarrison m add words which were missed in the version that I looked at. No change in mathematics was made, |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Sepia eyelid shape.theora.ogv|thumb|right|250px|The W-shaped pupil of the cuttlefish dilating when the lights are turned off]] | |||
[[File:Halogenlight.JPG|thumb|right|medical [[Halogen lamp|halogen penlight]] to observe Pupillary light reflex]] | |||
The '''pupillary light reflex''' ('''PLR''') is a [[reflex]] that controls the diameter of the [[pupil]], in response to the intensity ([[luminance]]) of light that falls on the [[retina]] of the [[human eye|eye]], thereby assisting in [[Adaptation (eye)|adaptation]] to various levels of darkness and light. Greater intensity light causes the pupil to become smaller ([[miosis|miosis/myosis]]) (allowing less light in), whereas lower intensity light causes the pupil to become larger (allowing more light in). Thus, the pupillary light reflex regulates the intensity of light entering the eye.<ref name="Purves" >{{cite book | author = Purves, Dale, George J. Augustine, David Fitzpatrick, William C. Hall, Anthony-Samuel LaMantia, James O. McNamara, and Leonard E. White | title = Neuroscience. 4th ed. | publisher = Sinauer Associates | pages = 290–1 | year = 2008 | isbn = 978-0-87893-697-7}}</ref> | |||
==Mechanism== | |||
[[Image:Ciliary ganglion pathways.png|thumb|400px|Pathways in the [[Ciliary ganglion]]. Green = parasympathetic; Red = sympathetic; Blue = sensory]] | |||
The [[optic nerve]], or more precisely, the [[photosensitive ganglion cell]]s through the [[retinohypothalamic tract]], is responsible for the [[afferent limb]] of the pupillary reflex - it senses the incoming light. The [[oculomotor nerve]] is responsible for the [[efferent limb]] of the pupillary reflex - it drives the muscles that constrict the pupil.<ref name="Purves" /> | |||
===Neuron 1=== | |||
The pupillary reflex pathway begins with the photosensitive retinal [[ganglion cell]]s, which convey information to the [[optic nerve]] (via the [[optic disc]]). The optic nerve connects to the [[Pretectum|pretectal nucleus]] of the upper [[midbrain]], bypassing the [[lateral geniculate nucleus]] and the [[primary visual cortex]]. | |||
These "intrinsic photosensitive ganglion cells" are also referred to as "[[melanopsin]]-containing" cells, and they influence the circadian rhythms and the pupillary light reflex. | |||
===Neuron 2=== | |||
From the pretectal nucleus, [[axon]]s connect to neurons in the [[Edinger-Westphal nucleus]], whose axons run along both the left and right [[oculomotor nerve]]s. | |||
===Neuron 3=== | |||
Parasympathetic neurons from the oculomotor nerve [[synapse]] on [[ciliary ganglion]] neurons. | |||
===Neuron 4=== | |||
Short ciliary nerves leave the ciliary ganglion to innervate the [[Iris sphincter muscle]] of the [[Iris (anatomy)|iris]].<ref name="Purves" /> | |||
==A Mathematical Description== | |||
Pupillary Light Reflex is modeled as a physiologically-based non-linear delay differential equation that describes the changes in the pupil diameter as a function of the environment lighting:<ref>Pamplona, V. F., Oliveira, M. M., and Baranoski, G. V. G. (2009). Photorealistic models for pupil light reflex and iridal pattern deformation. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 4 (Aug. 2009), 106:1-106:12. DOI= http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1559755.1559763</ref> | |||
<math> | |||
M(D) = atanh \left( \frac{D-4.9}{3} \right) | |||
</math> | |||
<math> | |||
\frac{dM}{dD}\frac{dD}{dt} + 2.3026 \; atanh \left( \frac{D-4.9}{3} \right) = 5.2 - 0.45 \; ln \left[\frac{ \Phi (t - \tau) }{4.8118~\times~10^{-10}} \right] \;\; | |||
</math> | |||
where <math>D</math> is the pupil diameter measured in millimeters and <math> \Phi(t - \tau) </math> is the luminous intensity reaching the retina in a time <math>t</math>, which can be described as <math>\Phi = IA</math>: luminance reaching the eye in lumens/mm<sup>2</sup> times the pupil area in mm<sup>2</sup>. <math>\tau</math> is the pupillary latency, a time delay between the instant in which the light pulse reaches the retina and the beginning of iridal reaction due nerve transmission, neuro-muscular excitation and activation delays. <math>dM</math>, <math>dD</math> and <math>dt</math> are the derivatives for the <math>M</math> function, pupil diameter <math>D</math> and time <math>t</math>. | |||
Since the pupil constriction velocity is approximately 3 times faster than (re)dilation velocity,<ref>{{cite journal | doi = 10.1136/bjo.65.11.754 | last = Ellis | first = C. J. | title = The pupillary light reflex in normal subjects| journal = British Journal of Ophthalmology | volume = 65 | issue = 11 | pages = 754–759 | year = 1981 | pmid = 7326222 | pmc = 1039657}}</ref> different step sizes in the numerical solver simulation must be used: | |||
<math>dt_{c} = \frac{T_{c} - T_{p}}{S}</math> | |||
<math>dt_{d} = \frac{T_{c} - T_{p}}{3S}</math> | |||
where <math>dt_{c}</math> and <math>dt_{d}</math> are respectively the <math>dt</math> for constriction and dilation measured in milliseconds, <math>Tc</math> and <math>Tp</math> are respectively the current and previous simulation times (times since the simulation started) measured in milliseconds, <math>S</math> is a constant that affects the constriction/dilation velocity and varies among individuals. | |||
The higher the <math>S</math> value, the smaller the time step used in the simulation and, consequently, the smaller the pupil constriction/dilation velocity. | |||
In order to improve the realism of the resulting simulations, the hippus effect can be approximated by adding small random variations to the environment light (in the range of 0.05 Hz to 0.3 Hz) as proposed by.<ref>Stark, L. W. (1939). Stability, Oscillations, and Noise in the Human Pupil Servomechanism. Proc. of the IRE, [S.l.], v.47, n.11, p.1925–1939</ref> | |||
==Clinical significance== | |||
In addition to controlling the amount of light that enters the eye, the pupillary light reflex provides a useful diagnostic tool. It allows for testing the integrity of the [[Sensory system|sensory]] and [[Motor system|motor]] functions of the eye.<ref name="Purves" /> | |||
Under normal conditions, the pupils of both eyes respond identically to a light [[Stimulus (physiology)|stimulus]], regardless of which eye is being stimulated. Light entering one eye produces a constriction of the pupil of that eye, the direct response, as well as a constriction of the pupil of the unstimulated eye, the [[consensual response]]. Comparing these two responses in both eyes is helpful in locating a [[lesion]].<ref name="Purves" /><ref name="url">{{cite web |url=http://www.med.yale.edu/caim/cnerves/cn3/cn3_12.html |title=Cranial Nerve III—Oculomotor Nerve |work=yale.edu |accessdate=2008-07-27}}</ref> | |||
For example, a direct response in the right pupil without a consensual response in the left pupil suggests a problem with the motor connection to the left pupil (perhaps as a result of damage to the [[oculomotor nerve]] or [[Edinger-Westphal nucleus]] of the brainstem). Lack of response to light stimulation of the right eye if both eyes respond normally to stimulation of the left eye indicates damage to the sensory input from the right eye (perhaps to the right retina or [[optic nerve]]).<ref name="Purves" /> | |||
[[Emergency room]] physicians routinely assess the pupillary reflex because it is useful for gauging [[brain stem]] function. Normally, pupils react (i.e. constrict) equally. Lack of the pupillary reflex or an abnormal pupillary reflex can be caused by optic nerve damage, oculomotor nerve damage, [[brain stem death]] and depressant drugs, such as [[barbiturates]]. | |||
Normally, both pupils should constrict with light shone into either eye alone. On testing each reflex for each eye, several patterns are possible.<ref>{{cite book | last = Colman | first = Andrew M. | title = [[A Dictionary of Psychology]] | publisher = [[Oxford University Press, USA]] |date=August 2001 | isbn = 0-19-866211-4 }}</ref> | |||
*[[Optic nerve]] damage on one side: (Example in parens.: Left optic nerve lesion) | |||
**The [[ipsilateral]] direct reflex is lost (Example: when the left eye is stimulated, neither pupil constricts, as no signals reach the brain from the left eye due to its damaged optic nerve) | |||
**The ipsilateral consensual reflex is intact (because light shone into the right eye can signal to the brain, causing constriction of both pupils via the normal oculomotor nerves) | |||
**The contralateral direct reflex is intact (because light shone into the right eye can signal to the brain, causing constriction of both pupils via the normal oculomotor nerves) | |||
**The contralateral consensual reflex is lost (because light shone into the eye on the damaged side cannot signal to the brain; therefore, despite the right eye's motor pathway (oculomotor nerve) being intact, no signals from the left eye are able to stimulate it due to the damage to the sensory pathway (optic nerve) of the left eye) | |||
*[[Oculomotor nerve]] damage on one side: (Example in parens: Left oculomotor lesion) | |||
**The ipsilateral direct reflex is lost (Example: when the left eye is stimulated, only the right pupil constricts) | |||
**The ipsilateral consensual reflex is lost (Example: when the right eye is stimulated, only the right pupil constricts) | |||
**The contralateral direct reflex is intact (because light shone into both eyes can still signal to the brain, and the pupil on the undamaged side will still be able to constrict via its normal oculomotor nerve) | |||
**The contralateral consensual reflex is intact (because light shone into the left eye can still signal to the brain via the normal optic nerve, causing attempted constriction of both pupils; the contralateral pupil constricts via its normal oculomotor nerve, but the ipsilateral pupil is unable to constrict due to its damaged oculomotor nerve) | |||
==See also== | |||
*[[Pupil]] | |||
*[[Pupillary response]] | |||
*[[Slit lamp]] | |||
==References== | |||
{{reflist|1}} | |||
==External links== | |||
*[http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/hyperbrain/anim/reflex.html Animation of pupillary light reflex] | |||
*{{MeshName|Reflex,+Pupillary}} | |||
*[http://cim.ucdavis.edu/EyeRelease/Interface/TopFrame.htm A pupil examination simulator], demonstrating the changes in pupil reactions for various nerve lesions. | |||
{{Reflex}} | |||
{{Visual system}} | |||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pupillary Light Reflex}} | |||
[[Category:Ophthalmology]] | |||
[[Category:Reflexes]] | |||
Revision as of 23:48, 20 December 2013
File:Sepia eyelid shape.theora.ogv

The pupillary light reflex (PLR) is a reflex that controls the diameter of the pupil, in response to the intensity (luminance) of light that falls on the retina of the eye, thereby assisting in adaptation to various levels of darkness and light. Greater intensity light causes the pupil to become smaller (miosis/myosis) (allowing less light in), whereas lower intensity light causes the pupil to become larger (allowing more light in). Thus, the pupillary light reflex regulates the intensity of light entering the eye.[1]
Mechanism
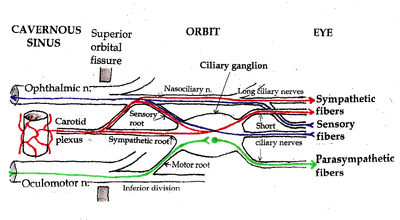
The optic nerve, or more precisely, the photosensitive ganglion cells through the retinohypothalamic tract, is responsible for the afferent limb of the pupillary reflex - it senses the incoming light. The oculomotor nerve is responsible for the efferent limb of the pupillary reflex - it drives the muscles that constrict the pupil.[1]
Neuron 1
The pupillary reflex pathway begins with the photosensitive retinal ganglion cells, which convey information to the optic nerve (via the optic disc). The optic nerve connects to the pretectal nucleus of the upper midbrain, bypassing the lateral geniculate nucleus and the primary visual cortex.
These "intrinsic photosensitive ganglion cells" are also referred to as "melanopsin-containing" cells, and they influence the circadian rhythms and the pupillary light reflex.
Neuron 2
From the pretectal nucleus, axons connect to neurons in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus, whose axons run along both the left and right oculomotor nerves.
Neuron 3
Parasympathetic neurons from the oculomotor nerve synapse on ciliary ganglion neurons.
Neuron 4
Short ciliary nerves leave the ciliary ganglion to innervate the Iris sphincter muscle of the iris.[1]
A Mathematical Description
Pupillary Light Reflex is modeled as a physiologically-based non-linear delay differential equation that describes the changes in the pupil diameter as a function of the environment lighting:[2]
where is the pupil diameter measured in millimeters and is the luminous intensity reaching the retina in a time , which can be described as : luminance reaching the eye in lumens/mm2 times the pupil area in mm2. is the pupillary latency, a time delay between the instant in which the light pulse reaches the retina and the beginning of iridal reaction due nerve transmission, neuro-muscular excitation and activation delays. , and are the derivatives for the function, pupil diameter and time .
Since the pupil constriction velocity is approximately 3 times faster than (re)dilation velocity,[3] different step sizes in the numerical solver simulation must be used:
where and are respectively the for constriction and dilation measured in milliseconds, and are respectively the current and previous simulation times (times since the simulation started) measured in milliseconds, is a constant that affects the constriction/dilation velocity and varies among individuals. The higher the value, the smaller the time step used in the simulation and, consequently, the smaller the pupil constriction/dilation velocity.
In order to improve the realism of the resulting simulations, the hippus effect can be approximated by adding small random variations to the environment light (in the range of 0.05 Hz to 0.3 Hz) as proposed by.[4]
Clinical significance
In addition to controlling the amount of light that enters the eye, the pupillary light reflex provides a useful diagnostic tool. It allows for testing the integrity of the sensory and motor functions of the eye.[1]
Under normal conditions, the pupils of both eyes respond identically to a light stimulus, regardless of which eye is being stimulated. Light entering one eye produces a constriction of the pupil of that eye, the direct response, as well as a constriction of the pupil of the unstimulated eye, the consensual response. Comparing these two responses in both eyes is helpful in locating a lesion.[1][5]
For example, a direct response in the right pupil without a consensual response in the left pupil suggests a problem with the motor connection to the left pupil (perhaps as a result of damage to the oculomotor nerve or Edinger-Westphal nucleus of the brainstem). Lack of response to light stimulation of the right eye if both eyes respond normally to stimulation of the left eye indicates damage to the sensory input from the right eye (perhaps to the right retina or optic nerve).[1]
Emergency room physicians routinely assess the pupillary reflex because it is useful for gauging brain stem function. Normally, pupils react (i.e. constrict) equally. Lack of the pupillary reflex or an abnormal pupillary reflex can be caused by optic nerve damage, oculomotor nerve damage, brain stem death and depressant drugs, such as barbiturates.
Normally, both pupils should constrict with light shone into either eye alone. On testing each reflex for each eye, several patterns are possible.[6]
- Optic nerve damage on one side: (Example in parens.: Left optic nerve lesion)
- The ipsilateral direct reflex is lost (Example: when the left eye is stimulated, neither pupil constricts, as no signals reach the brain from the left eye due to its damaged optic nerve)
- The ipsilateral consensual reflex is intact (because light shone into the right eye can signal to the brain, causing constriction of both pupils via the normal oculomotor nerves)
- The contralateral direct reflex is intact (because light shone into the right eye can signal to the brain, causing constriction of both pupils via the normal oculomotor nerves)
- The contralateral consensual reflex is lost (because light shone into the eye on the damaged side cannot signal to the brain; therefore, despite the right eye's motor pathway (oculomotor nerve) being intact, no signals from the left eye are able to stimulate it due to the damage to the sensory pathway (optic nerve) of the left eye)
- Oculomotor nerve damage on one side: (Example in parens: Left oculomotor lesion)
- The ipsilateral direct reflex is lost (Example: when the left eye is stimulated, only the right pupil constricts)
- The ipsilateral consensual reflex is lost (Example: when the right eye is stimulated, only the right pupil constricts)
- The contralateral direct reflex is intact (because light shone into both eyes can still signal to the brain, and the pupil on the undamaged side will still be able to constrict via its normal oculomotor nerve)
- The contralateral consensual reflex is intact (because light shone into the left eye can still signal to the brain via the normal optic nerve, causing attempted constriction of both pupils; the contralateral pupil constricts via its normal oculomotor nerve, but the ipsilateral pupil is unable to constrict due to its damaged oculomotor nerve)
See also
References
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.
External links
- Animation of pupillary light reflex
- Template:MeshName
- A pupil examination simulator, demonstrating the changes in pupil reactions for various nerve lesions.
Template:Reflex Template:Visual system
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ Pamplona, V. F., Oliveira, M. M., and Baranoski, G. V. G. (2009). Photorealistic models for pupil light reflex and iridal pattern deformation. ACM Trans. Graph. 28, 4 (Aug. 2009), 106:1-106:12. DOI= http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1559755.1559763
- ↑ One of the biggest reasons investing in a Singapore new launch is an effective things is as a result of it is doable to be lent massive quantities of money at very low interest rates that you should utilize to purchase it. Then, if property values continue to go up, then you'll get a really high return on funding (ROI). Simply make sure you purchase one of the higher properties, reminiscent of the ones at Fernvale the Riverbank or any Singapore landed property Get Earnings by means of Renting
In its statement, the singapore property listing - website link, government claimed that the majority citizens buying their first residence won't be hurt by the new measures. Some concessions can even be prolonged to chose teams of consumers, similar to married couples with a minimum of one Singaporean partner who are purchasing their second property so long as they intend to promote their first residential property. Lower the LTV limit on housing loans granted by monetary establishments regulated by MAS from 70% to 60% for property purchasers who are individuals with a number of outstanding housing loans on the time of the brand new housing purchase. Singapore Property Measures - 30 August 2010 The most popular seek for the number of bedrooms in Singapore is 4, followed by 2 and three. Lush Acres EC @ Sengkang
Discover out more about real estate funding in the area, together with info on international funding incentives and property possession. Many Singaporeans have been investing in property across the causeway in recent years, attracted by comparatively low prices. However, those who need to exit their investments quickly are likely to face significant challenges when trying to sell their property – and could finally be stuck with a property they can't sell. Career improvement programmes, in-house valuation, auctions and administrative help, venture advertising and marketing, skilled talks and traisning are continuously planned for the sales associates to help them obtain better outcomes for his or her shoppers while at Knight Frank Singapore. No change Present Rules
Extending the tax exemption would help. The exemption, which may be as a lot as $2 million per family, covers individuals who negotiate a principal reduction on their existing mortgage, sell their house short (i.e., for lower than the excellent loans), or take part in a foreclosure course of. An extension of theexemption would seem like a common-sense means to assist stabilize the housing market, but the political turmoil around the fiscal-cliff negotiations means widespread sense could not win out. Home Minority Chief Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) believes that the mortgage relief provision will be on the table during the grand-cut price talks, in response to communications director Nadeam Elshami. Buying or promoting of blue mild bulbs is unlawful.
A vendor's stamp duty has been launched on industrial property for the primary time, at rates ranging from 5 per cent to 15 per cent. The Authorities might be trying to reassure the market that they aren't in opposition to foreigners and PRs investing in Singapore's property market. They imposed these measures because of extenuating components available in the market." The sale of new dual-key EC models will even be restricted to multi-generational households only. The models have two separate entrances, permitting grandparents, for example, to dwell separately. The vendor's stamp obligation takes effect right this moment and applies to industrial property and plots which might be offered inside three years of the date of buy. JLL named Best Performing Property Brand for second year running
The data offered is for normal info purposes only and isn't supposed to be personalised investment or monetary advice. Motley Fool Singapore contributor Stanley Lim would not personal shares in any corporations talked about. Singapore private home costs increased by 1.eight% within the fourth quarter of 2012, up from 0.6% within the earlier quarter. Resale prices of government-built HDB residences which are usually bought by Singaporeans, elevated by 2.5%, quarter on quarter, the quickest acquire in five quarters. And industrial property, prices are actually double the levels of three years ago. No withholding tax in the event you sell your property. All your local information regarding vital HDB policies, condominium launches, land growth, commercial property and more
There are various methods to go about discovering the precise property. Some local newspapers (together with the Straits Instances ) have categorised property sections and many local property brokers have websites. Now there are some specifics to consider when buying a 'new launch' rental. Intended use of the unit Every sale begins with 10 p.c low cost for finish of season sale; changes to 20 % discount storewide; follows by additional reduction of fiftyand ends with last discount of 70 % or extra. Typically there is even a warehouse sale or transferring out sale with huge mark-down of costs for stock clearance. Deborah Regulation from Expat Realtor shares her property market update, plus prime rental residences and houses at the moment available to lease Esparina EC @ Sengkang - ↑ Stark, L. W. (1939). Stability, Oscillations, and Noise in the Human Pupil Servomechanism. Proc. of the IRE, [S.l.], v.47, n.11, p.1925–1939
- ↑ Template:Cite web
- ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534

![{\frac {dM}{dD}}{\frac {dD}{dt}}+2.3026\;atanh\left({\frac {D-4.9}{3}}\right)=5.2-0.45\;ln\left[{\frac {\Phi (t-\tau )}{4.8118~\times ~10^{{-10}}}}\right]\;\;](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/15dfced06f1cff1f1b2a3708031643ee40cb9f92)















