Woldemar Voigt: Difference between revisions
en>Henry McClean added ka-wiki |
en>Rjwilmsi m Journal cites, added 1 DOI using AWB (9888) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{About|dispersion of waves in optics|other forms of dispersion|Dispersion (disambiguation)}} | |||
[[File:Prism rainbow schema.png|thumb|right|In a [[dispersive prism]], material dispersion (a [[wavelength]]-dependent [[refractive index]]) causes different colors to [[refraction|refract]] at different angles, splitting white light into a [[rainbow]].]] | |||
[[File:Light dispersion of a compact fluorescent lamp seen through an Amici direct-vision prism PNr°0114.jpg|thumb|A [[compact fluorescent lamp]] seen through an [[Amici prism]]]] | |||
In [[optics]], '''dispersion''' is the phenomenon in which the [[phase velocity]] of a wave depends on its frequency,<ref>{{cite book | |||
|last = Born | |||
|first = Max | |||
|authorlink = Max Born | |||
|last2 = Wolf | |||
|first2 = Emil | |||
|title = Principles of Optics | |||
|publisher = [[Cambridge University Press]] | |||
|date = October 1999 | |||
|location = Cambridge | |||
|pages = 14–24 | |||
|isbn = 0-521-64222-1}}</ref> or alternatively when the [[group velocity]] depends on the frequency. | |||
Media having such a property are termed ''dispersive media''. Dispersion is sometimes called '''''chromatic'' dispersion''' to emphasize its wavelength-dependent nature, or '''group-velocity dispersion''' ('''GVD''') to emphasize the role of the group velocity. | |||
Dispersion is most often described for [[light]] waves, but it may occur for any kind of wave that interacts with a medium or passes through an inhomogeneous geometry (e.g., a [[waveguide]]), such as [[sound]] waves. A material's dispersion is measured by its [[Abbe number]], ''V'', with low Abbe numbers corresponding to strong dispersion. | |||
== Examples of dispersion == | |||
The most familiar example of dispersion is probably a [[rainbow]], in which dispersion causes the spatial separation of a white light into components of different [[wavelengths]] (different [[color]]s). However, dispersion also has an effect in many other circumstances: for example, GVD causes [[Pulse (signal processing)|pulses]] to spread in [[optical fiber]]s, degrading signals over long distances; also, a cancellation between group-velocity dispersion and [[nonlinear]] effects leads to [[soliton]] waves. | |||
== Sources of dispersion == | |||
There are generally two sources of dispersion: material dispersion and waveguide dispersion. '''Material dispersion''' comes from a frequency-dependent response of a material to waves. For example, material dispersion leads to undesired [[chromatic aberration]] in a [[lens (optics)|lens]] or the separation of colors in a [[Dispersive prism|prism]]. '''Waveguide dispersion''' occurs when the speed of a wave in a waveguide (such as an optical fiber) depends on its frequency for geometric reasons, independent of any frequency dependence of the materials from which it is constructed. More generally, "waveguide" dispersion can occur for waves propagating through any inhomogeneous structure (e.g., a [[photonic crystal]]), whether or not the waves are confined to some region. In general, ''both'' types of dispersion may be present, although they are not strictly additive. Their combination leads to signal degradation in [[optical fiber]]s for [[telecommunication]]s, because the varying delay in arrival time between different components of a signal "smears out" the signal in time. | |||
== Material dispersion in optics == | |||
[[File:Dispersion-curve.png|right|thumb|320px|The variation of refractive index vs. vacuum wavelength for various glasses. The wavelengths of visible light are shaded in red.]] | |||
[[File:Spidergraph Dispersion.GIF|320px|thumb|Influences of selected glass component additions on the mean dispersion of a specific base glass (n<sub>F</sub> valid for λ = 486 nm (blue), n<sub>C</sub> valid for λ = 656 nm (red))<ref>[http://glassproperties.com/dispersion/ Calculation of the Mean Dispersion of Glasses]</ref>]] | |||
Material dispersion can be a desirable or undesirable effect in optical applications. The dispersion of light by glass prisms is used to construct [[spectrometer]]s and [[spectroradiometer]]s. [[Holographic]] gratings are also used, as they allow more accurate discrimination of wavelengths. However, in lenses, dispersion causes [[chromatic aberration]], an undesired effect that may degrade images in microscopes, telescopes and photographic objectives. | |||
The ''[[phase velocity]]'', ''v'', of a wave in a given uniform medium is given by | |||
:<math>v = \frac{c}{n}</math> | |||
where ''c'' is the [[speed of light]] in a vacuum and ''n'' is the [[refractive index]] of the medium. | |||
In general, the refractive index is some function of the frequency ''f'' of the light, thus ''n'' = ''n''(''f''), or alternatively, with respect to the wave's wavelength ''n'' = ''n''(''λ''). The wavelength dependence of a material's refractive index is usually quantified by its [[Abbe number]] or its coefficients in an empirical formula such as the [[Cauchy's equation|Cauchy]] or [[Sellmeier equation]]s. | |||
Because of the [[Kramers–Kronig relation]]s, the wavelength dependence of the real part of the refractive index is related to the material [[absorption (electromagnetic radiation)|absorption]], described by the imaginary part of the refractive index (also called the [[refractive index#Dispersion and absorption|extinction coefficient]]). In particular, for non-magnetic materials ([[Permeability (electromagnetism)|μ]] = [[magnetic constant|μ<sub>0</sub>]]), the [[Linear response function|susceptibility]] <math>\chi</math> that appears in the Kramers–Kronig relations is the [[electric susceptibility]] <math>\chi_e = n^2 - 1</math>. | |||
The most commonly seen consequence of dispersion in optics is the separation of [[white light]] into a [[optical spectrum|color spectrum]] by a [[triangular prism (optics)|prism]]. From [[Snell's law]] it can be seen that the angle of [[refraction]] of light in a prism depends on the refractive index of the prism material. Since that refractive index varies with wavelength, it follows that the angle that the light is refracted by will also vary with wavelength, causing an angular separation of the colors known as ''angular dispersion''. | |||
For visible light, refraction indices ''n'' of most transparent materials (e.g., air, glasses) decrease with increasing wavelength ''λ'': | |||
:<math>1 < n(\lambda_{\rm red}) < n(\lambda_{\rm yellow}) < n(\lambda_{\rm blue})\ ,</math> | |||
or alternatively: | |||
:<math>\frac{{\rm d}n}{{\rm d}\lambda} < 0.</math> | |||
In this case, the medium is said to have ''normal dispersion''. Whereas, if the index increases with increasing wavelength (which is typically the case for [[X-ray]]s), the medium is said to have ''anomalous dispersion''. | |||
At the interface of such a material with air or vacuum (index of ~1), Snell's law predicts that light incident at an angle ''θ'' to the [[surface normal|normal]] will be refracted at an angle arcsin(sin(''θ'')/''n''). Thus, blue light, with a higher refractive index, will be bent more strongly than red light, resulting in the well-known [[rainbow]] pattern. | |||
==Group and phase velocity==<!-- This section is linked from [[Speed of sound]] --> | |||
{{merge section from|Group delay and phase delay#Group delay in optics|date=September 2013}} | |||
Another consequence of dispersion manifests itself as a temporal effect. The formula ''v'' = ''c'' / ''n'' calculates the ''phase velocity'' of a wave; this is the [[velocity]] at which the ''[[phase (waves)|phase]]'' of any one frequency component of the wave will propagate. This is not the same as the ''[[group velocity]]'' of the wave, that is the rate at which changes in [[amplitude]] (known as the ''envelope'' of the wave) will propagate. For a homogeneous medium, the group velocity ''v''<sub>g</sub> is related to the phase velocity by (here λ is the wavelength in vacuum, not in the medium): | |||
:<math>v_g = c \left( n - \lambda \frac{dn}{d\lambda} \right)^{-1}.</math> | |||
The group velocity ''v''<sub>g</sub> is often thought of as the velocity at which energy or information is conveyed along the wave. In most cases this is true, and the group velocity can be thought of as the ''[[signal velocity]]'' of the waveform. In some unusual circumstances, called cases of anomalous dispersion, the rate of change of the index of refraction with respect to the wavelength changes sign, in which case it is possible for the group velocity to exceed the speed of light (''v''<sub>g</sub> > ''c''). Anomalous dispersion occurs, for instance, where the wavelength of the light is close to an [[absorption (optics)|absorption]] resonance of the medium. When the dispersion is anomalous, however, group velocity is no longer an indicator of signal velocity. Instead, a signal travels at the speed of the wavefront, which is ''c'' irrespective of the index of refraction.<ref>Brillouin, Léon. Wave Propagation and Group Velocity. (Academic Press: San Diego, 1960). See esp. Ch. 2 by A. Sommerfeld.</ref> Recently, it has become possible to create gases in which the group velocity is not only larger than the speed of light, but even negative. In these cases, a pulse can appear to exit a medium before it enters.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Wang, L.J., Kuzmich, A., and Dogariu, A.|title=Gain-assisted superluminal light propagation|journal=Nature|volume=406|page=277|year=2000|bibcode = 2000Natur.406..277W | doi=10.1038/35018520 | issue=6793}}</ref> Even in these cases, however, a signal travels at, or less than, the speed of light, as demonstrated by Stenner, et al.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Stenner, M. D., Gauthier, D. J., and Neifeld, M. A.|title=The speed of information in a 'fast-light' optical medium|journal=Nature|volume=425 |year=2003|bibcode = 2003Natur.425..695S |doi = 10.1038/nature02016|issue=6959|pmid=14562097|pages=695–8}}</ref> | |||
The group velocity itself is usually a function of the wave's frequency. This results in '''group velocity dispersion''' (GVD), which causes a short pulse of light to spread in time as a result of different frequency components of the pulse travelling at different velocities. GVD is often quantified as the ''[[group delay]] dispersion parameter'' (again, this formula is for a uniform medium only): | |||
:<math>D = - \frac{\lambda}{c} \, \frac{d^2 n}{d \lambda^2}. </math> | |||
If ''D'' is less than zero, the medium is said to have ''positive dispersion''. If ''D'' is greater than zero, the medium has ''negative dispersion''. If a light pulse is propagated through a normally dispersive medium, the result is the higher frequency components travel slower than the lower frequency components. The pulse therefore becomes ''positively [[chirp]]ed'', or ''up-chirped'', increasing in frequency with time. Conversely, if a pulse travels through an anomalously dispersive medium, high frequency components travel faster than the lower ones, and the pulse becomes ''negatively [[chirp]]ed'', or ''down-chirped'', decreasing in frequency with time. | |||
The result of GVD, whether negative or positive, is ultimately temporal spreading of the pulse. This makes dispersion management extremely important in optical communications systems based on optical fiber, since if dispersion is too high, a group of pulses representing a bit-stream will spread in time and merge, rendering the bit-stream unintelligible. This limits the length of fiber that a signal can be sent down without regeneration. One possible answer to this problem is to send signals down the optical fibre at a wavelength where the GVD is zero (e.g., around 1.3–1.5 μm in [[silica]] [[fibres]]), so pulses at this wavelength suffer minimal spreading from dispersion—in practice, however, this approach causes more problems than it solves because zero GVD unacceptably amplifies other nonlinear effects (such as [[four wave mixing]]). Another possible option is to use [[soliton (optics)|soliton]] pulses in the regime of anomalous dispersion, a form of optical pulse which uses a [[nonlinear optics|nonlinear optical]] effect to self-maintain its shape—solitons have the practical problem, however, that they require a certain power level to be maintained in the pulse for the nonlinear effect to be of the correct strength. Instead, the solution that is currently used in practice is to perform dispersion compensation, typically by matching the fiber with another fiber of opposite-sign dispersion so that the dispersion effects cancel; such compensation is ultimately limited by nonlinear effects such as [[self-phase modulation]], which interact with dispersion to make it very difficult to undo. | |||
Dispersion control is also important in [[laser]]s that produce [[ultrashort pulse|short pulses]]. The overall dispersion of the [[laser construction|optical resonator]] is a major factor in determining the duration of the pulses emitted by the laser. A pair of [[Prism (optics)|prisms]] can be arranged to produce net negative dispersion, which can be used to balance the usually positive dispersion of the laser medium. [[Diffraction grating]]s can also be used to produce dispersive effects; these are often used in high-power laser amplifier systems. Recently, an alternative to prisms and gratings has been developed: [[chirped mirror]]s. These dielectric mirrors are coated so that different wavelengths have different penetration lengths, and therefore different group delays. The coating layers can be tailored to achieve a net negative dispersion. | |||
== Dispersion in waveguides == | |||
[[Optical fibers]], which are used in telecommunications, are among the most abundant types of waveguides. Dispersion in these fibers is one of the limiting factors that determine how much data can be transported on a single fiber. | |||
The [[transverse mode]]s for waves confined laterally within a [[waveguide]] generally have different speeds (and field patterns) depending upon their frequency (that is, on the relative size of the wave, the wavelength) compared to the size of the waveguide. | |||
In general, for a waveguide mode with an [[angular frequency]] ω(β) at a [[propagation constant]] β (so that the electromagnetic fields in the propagation direction ''(z)'' oscillate proportional to <math>e^{i(\beta z - \omega t)}</math>), the group-velocity [[dispersion parameter]] ''D'' is defined as:<ref>Rajiv Ramaswami and Kumar N. Sivarajan, ''Optical Networks: A Practical Perspective'' (Academic Press: London 1998).</ref> | |||
:<math>D = -\frac{2\pi c}{\lambda^2} \frac{d^2 \beta}{d\omega^2} = \frac{2\pi c}{v_g^2 \lambda^2} \frac{dv_g}{d\omega}</math> | |||
where <math>\lambda = 2\pi c/\omega</math> is the vacuum wavelength and <math>v_g = d\omega/d\beta</math> is the group velocity. This formula generalizes the one in the previous section for homogeneous media, and includes both waveguide dispersion and material dispersion. The reason for defining the dispersion in this way is that |''D''| is the (asymptotic) temporal pulse spreading <math>\Delta t</math> per unit bandwidth | |||
<math>\Delta\lambda</math> per unit distance travelled, commonly reported in [[picosecond|ps]] / [[nanometre|nm]] km for optical fibers. | |||
A similar effect due to a somewhat different phenomenon is [[modal dispersion]], caused by a waveguide having multiple modes at a given frequency, each with a different speed. A special case of this is [[polarization mode dispersion]] (PMD), which comes from a superposition of two modes that travel at different speeds due to random imperfections that break the symmetry of the waveguide. [[Modal dispersion]] can also be used to generate large, tunable group delay dispersion in a compact footprint using [[chromo-modal dispersion]].<ref>E.D. Diebold et al., "Giant tunable optical dispersion using chromo-modal excitation of a multimode waveguide," Optics Express 19 (24) 2011</ref> | |||
== Higher-order dispersion over broad bandwidths == | |||
When a broad range of frequencies (a broad bandwidth) is present in a single wavepacket, such as in an [[ultrashort pulse]] or a [[chirp]]ed pulse or other forms of [[spread spectrum]] transmission, it may not be accurate to approximate the dispersion by a constant over the entire bandwidth, and more complex calculations are required to compute effects such as pulse spreading. | |||
In particular, the dispersion parameter ''D'' defined above is obtained from only one derivative of the group velocity. Higher derivatives are known as ''higher-order dispersion''.<ref>[http://www.rp-photonics.com/chromatic_dispersion.html Chromatic Dispersion], ''Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology'' (Wiley, 2008).</ref> These terms are simply a [[Taylor series]] expansion of the [[dispersion relation]] <math>\beta(\omega)</math> of the medium or waveguide around some particular frequency. Their effects can be computed via numerical evaluation of [[Fourier transform]]s of the waveform, via integration of higher-order [[slowly varying envelope approximation]]s, by a [[split-step method]] (which can use the exact dispersion relation rather than a Taylor series), or by direct simulation of the full [[Maxwell's equations]] rather than an approximate envelope equation. | |||
== Dispersion in gemology == | |||
{|Class="wikitable sortable collapsible collapsed" style="float:right; text-align: center" | |||
|+Dispersion values of minerals<ref name=b1>{{cite book|author=Walter Schumann|title=Gemstones of the World: Newly Revised & Expanded Fourth Edition|url=http://books.google.com/books?id=V9PqVxpxeiEC&pg=PA42|accessdate=31 December 2011|year=2009|publisher=Sterling Publishing Company, Inc.|isbn=978-1-4027-6829-3|pages=41–2}}</ref> | |||
!Name !!B–G !!C–F | |||
|- | |||
|[[Cinnabar]] (HgS) || 0.40 || – | |||
|- | |||
|Synth. [[rutile]] || 0.330 || 0.190 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Rutile]] (TiO<sub>2</sub>) || 0.280 || 0.120–0.180 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Anatase]] (TiO<sub>2</sub>)|| 0.213–0.259 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Wulfenite]] || 0.203 || 0.133 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Vanadinite]] || 0.202 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Fabulite]] || 0.190 || 0.109 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Sphalerite]] (ZnS) || 0.156 || 0.088 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Sulfur]] (S) || 0.155 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Stibiotantalite]] || 0.146 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Goethite]] (FeO(OH)) || 0.14 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Brookite]] (TiO<sub>2</sub>) || 0.131 || 0.12–1.80 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Zincite]] (ZnO) || 0.127 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Linobate]] || 0.13 || 0.075 | |||
|- | |||
|Synth. [[moissanite]] (SiC) || 0.104 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Cassiterite]] (SnO<sub>2</sub>)|| 0.071 || 0.035 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Zirconia]] (ZrO<sub>2</sub>)|| 0.060 || 0.035 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Powellite]] (CaMoO<sub>4</sub>) || 0.058 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Andradite]] || 0.057 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Demantoid]] || 0.057 || 0.034 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Cerussite]] || 0.055 || 0.033–0.050 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Titanite]] || 0.051 || 0.019–0.038 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Benitoite]] || 0.046 || 0.026 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Anglesite]] || 0.044 || 0.025 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Diamond]] (C) || 0.044 || 0.025 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Flint glass]] || 0.041 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hyacinth (mineral)|Hyacinth]] || 0.039 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Jargoon]] || 0.039 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Starlite]] || 0.039 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Zircon]] (ZrSiO<sub>4</sub>)|| 0.039 || 0.022 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Gadolinium gallium garnet|GGG]] || 0.038 || 0.022 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Scheelite]] || 0.038 || 0.026 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Dioptase]] || 0.036 || 0.021 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Whewellite]] || 0.034 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Alabaster]] || 0.033 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Gypsum]] || 0.033 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Epidote]] || 0.03 || 0.012–0.027 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Achroite]] || 0.017 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Cordierite]] || 0.017 || 0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Danburite]] || 0.017 || 0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Dravite]] || 0.017 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Elbaite]] || 0.017 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Herderite]] || 0.017 || 0.008–0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hiddenite]] || 0.017 || 0.010 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Indicolite]] || 0.017 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Liddicoatite]] || 0.017 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Kunzite]] || 0.017 || 0.010 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Rubellite]] || 0.017 || 0.008–0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Schorl]] || 0.017 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Scapolite]] || 0.017 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Spodumene]] || 0.017 || 0.010 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Tourmaline]] || 0.017 || 0.009–0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Verdelite]] || 0.017 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Andalusite]] || 0.016 || 0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Baryte]] (BaSO<sub>4</sub>)|| 0.016 || 0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Euclase]] || 0.016 || 0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Alexandrite]] || 0.015 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Chrysoberyl]] || 0.015 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hambergite]] || 0.015 || 0.009–0.010 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Phenakite]] || 0.01 || 0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Rhodochrosite]] || 0.015 || 0.010–0.020 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Sillimanite]] || 0.015 || 0.009–0.012 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Smithsonite]] || 0.014–0.031 || 0.008–0.017 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Amblygonite]] || 0.014–0.015 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
| [[Aquamarine (gemstone)|Aquamarine]] || 0.014 || 0.009–0.013 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Beryl]] || 0.014 || 0.009–0.013 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Brazilianite]] || 0.014 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Celestine (mineral)|Celestine]] || 0.014 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Goshenite]] || 0.014 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Heliodor]] || 0.014 || 0.009–0.013 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Morganite]] || 0.014 || 0.009–0.013 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Pyroxmangite]] || 0.015 || – | |||
|- | |||
|Synth. [[scheelite]] || 0.015 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Dolomite]] || 0.013 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Magnesite]] (MgCO<sub>3</sub>)|| 0.012 || – | |||
|- | |||
|Synth. [[emerald]] || 0.012 || – | |||
|- | |||
|Synth. [[alexandrite]] || 0.011 || – | |||
|- | |||
|Synth. [[sapphire]] (Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>)|| 0.011 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Phosphophyllite]] || 0.010–0.011 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Enstatite]] || 0.010 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Anorthite]] || 0.009–0.010 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Actinolite]] || 0.009 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Jeremejevite]] || 0.009 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Nepheline]] || 0.008–0.009 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Apophyllite]] || 0.008 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hauyne]] || 0.008 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Natrolite]] || 0.008 || – | |||
|- | |||
|Synth. quartz (SiO<sub>2</sub>) || 0.008 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Aragonite]] || 0.007–0.012 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Augelite]] || 0.007 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Tanzanite]] || 0.030 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Thulite]] || 0.03 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Zoisite]] || 0.03 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[YAG]] || 0.028 || 0.015 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Almandine]] || 0.027 || 0.013–0.016 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hessonite]] || 0.027 || 0.013–0.015 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Spessartine]] || 0.027 || 0.015 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Uvarovite]] || 0.027 || 0.014–0.021 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Willemite]] || 0.027 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Pleonaste]] || 0.026 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Rhodolite]] || 0.026 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Boracite]] || 0.024 || 0.012 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Cryolite]] || 0.024 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Staurolite]] || 0.023 || 0.012–0.013 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Pyrope]] || 0.022 || 0.013–0.016 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Diaspore]] || 0.02 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Grossular]] || 0.020 || 0.012 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hemimorphite]] || 0.020 || 0.013 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Kyanite]] || 0.020 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Peridot]] || 0.020 || 0.012–0.013 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Spinel]] || 0.020 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Vesuvianite]] || 0.019–0.025 || 0.014 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Clinozoisite]] || 0.019 || 0.011–0.014 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Labradorite]] || 0.019 || 0.010 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Axinite]] || 0.018–0.020 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Ekanite]] || 0.018 || 0.012 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Kornerupine]] || 0.018 || 0.010 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Corundum]] (Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>)|| 0.018 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Rhodizite]] || 0.018 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Ruby]] (Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>)|| 0.018 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Sapphire]] (Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub>)|| 0.018 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Sinhalite]] || 0.018 || 0.010 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Sodalite]] || 0.018 || 0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|Synth. [[corundum]] || 0.018 || 0.011 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Diopside]] || 0.018–0.020 || 0.01 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Emerald]] || 0.014 || 0.009–0.013 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Topaz]] || 0.014 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Amethyst]] (SiO<sub>2</sub>)|| 0.013 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Anhydrite]] || 0.013 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Apatite]] || 0.013 || 0.010 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Apatite]] || 0.013 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Aventurine]] || 0.013 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Citrine]] || 0.013 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Morion (mineral)|Morion]] || 0.013 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Prasiolite]] || 0.013 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Quartz]] (SiO<sub>2</sub>)|| 0.013 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|Smoky quartz (SiO<sub>2</sub>)|| 0.013 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|Rose quartz (SiO<sub>2</sub>)|| 0.013 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Albite]] || 0.012 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Bytownite]] || 0.012 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Feldspar]] || 0.012 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Moonstone (gemstone)|Moonstone]] || 0.012 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Orthoclase]] || 0.012 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Pollucite]] || 0.012 || 0.007 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Sanidine]] || 0.012 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Sunstone]] || 0.012 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Beryllonite]] || 0.010 || 0.007 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Cancrinite]] || 0.010 || 0.008–0.009 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Leucite]] || 0.010 || 0.008 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Obsidian]] || 0.010 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Strontianite]] || 0.008–0.028 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Calcite]] (CaCO<sub>3</sub>) || 0.008–0.017 || 0.013–0.014 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Fluorite]] (CaF<sub>2</sub>)|| 0.007 || 0.004 | |||
|- | |||
|[[Hematite]] || 0.500 || – | |||
|- | |||
|Synth. [[cassiterite]] (SnO<sub>2</sub>)|| 0.041 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Gahnite]] || 0.019–0.021 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Datolite]] || 0.016 || – | |||
|- | |||
|[[Tremolite]] || 0.006–0.007 || – | |||
|} | |||
In the [[technical terminology]] of [[gemology]], ''dispersion'' is the difference in the refractive index of a material at the B and G (686.7 [[Nanometre|nm]] and 430.8 nm) or C and F (656.3 nm and 486.1 nm) [[fraunhofer line|Fraunhofer]] wavelengths, and is meant to express the degree to which a prism cut from the [[gemstone]] shows "fire", or color. Dispersion is a material property. Fire depends on the dispersion, the cut angles, the lighting environment, the refractive index, and the viewer.<ref name=b1 /> | |||
== Dispersion in imaging == | |||
In photographic and microscopic lenses, dispersion causes [[chromatic aberration]], which causes the different colors in the image not to overlap properly. Various techniques have been developed to counteract this, such as the use of [[achromat]]s, multielement lenses with glasses of different dispersion. They are constructed in such a way that the chromatic aberrations of the different parts cancel out. | |||
== Dispersion in pulsar timing == | |||
[[Pulsar]]s are spinning neutron stars that emit pulses at very regular intervals ranging from milliseconds to seconds. Astronomers believe that the pulses are emitted simultaneously over a wide range of frequencies. However, as observed on Earth, the components of each pulse emitted at higher radio frequencies arrive before those emitted at lower frequencies. This dispersion occurs because of the ionized component of the [[interstellar medium]], mainly the free electrons, which make the group velocity frequency dependent. The extra delay added at a frequency <math>\nu</math> is | |||
:<math>t = k_\mathrm{DM} \times \left(\frac{\mathrm{DM}}{\nu^2}\right)</math> | |||
where the dispersion constant <math>k_\mathrm{DM}</math> is given by | |||
:<math> k_\mathrm{DM} = \frac{k_e e^2}{2 \pi m_\mathrm{e}c} \simeq 4.149 \mathrm{GHz}^2\mathrm{pc}^{-1}\mathrm{cm}^3\mathrm{ms}</math>, | |||
and the dispersion measure ''DM'' is the column density of electrons — i.e. the number density of electrons <math>n_e</math> (electrons/cm<sup>3</sup>) integrated along the path traveled by the photon from the pulsar to the Earth — and is given by | |||
:<math>\mathrm{DM} = \int_0^d{n_e\;dl}</math> | |||
with units of [[parsec]]s per cubic centimetre (1pc/cm<sup>3</sup> = 30.857×10<sup>21</sup> m<sup>−2</sup>).<ref>Lorimer, D.R., and Kramer, M., ''Handbook of Pulsar Astronomy'', vol. 4 of Cambridge Observing Handbooks for Research Astronomers, ([[Cambridge University Press]], Cambridge, U.K.; New York, U.S.A, 2005), 1st edition.</ref> | |||
Typically for astronomical observations, this delay cannot be measured directly, since the emission time is unknown. What ''can'' be measured is the difference in arrival times at two different frequencies. The delay <math>\Delta T</math> between a high frequency <math>\nu_{hi}</math> and a low frequency <math>\nu_{lo}</math> component of a pulse will be | |||
:<math>\Delta t = k_\mathrm{DM} \times \mathrm{DM} \times \left( \frac{1}{\nu_{\mathrm{lo}}^2} - \frac{1}{\nu_{\mathrm{hi}}^2} \right)</math> | |||
Re-writing the above equation in terms of ''DM'' allows one to determine the ''DM'' by measuring pulse arrival times at multiple frequencies. This in turn can be used to study the interstellar medium, as well as allow for observations of pulsars at different frequencies to be combined. | |||
== See also == | |||
{{colbegin|3}} | |||
* [[Dispersion relation]] | |||
* [[Sellmeier equation]] | |||
* [[Cauchy's equation]] | |||
* [[Abbe number]] | |||
* [[Kramers–Kronig relations]] | |||
* [[Group delay]] | |||
* [[Calculation of glass properties]] incl. dispersion | |||
* [[Linear response function]] | |||
* [[Green–Kubo relations]] | |||
* [[Fluctuation theorem]] | |||
* [[Multiple-prism dispersion theory]] | |||
* [[Ultrashort pulse]] | |||
* [[Intramodal dispersion]] | |||
{{colend}} | |||
== References == | |||
<!-- ---------------------------------------------------------- | |||
See [[Wikipedia:Footnotes]] for a | |||
discussion of different citation methods and how to generate | |||
footnotes using the<ref>,</ref> and <reference /> tags | |||
----------------------------------------------------------- --> | |||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
== External links == | |||
{{Commons|Dispersion|Dispersion (optics)}} | |||
* [http://ioannis.virtualcomposer2000.com/spectroscope/characteristics.html Optical Characteristics of the SF10 Crystal Prism] | |||
* [http://ioannis.virtualcomposer2000.com/spectroscope/deviationangle.html Deviation Angle for a Prism] | |||
* [http://tosio.math.toronto.edu/wiki/index.php/Main_Page Dispersive Wiki] – discussing the mathematical aspects of dispersion. | |||
* [http://www.rp-photonics.com/dispersion.html Dispersion] – Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology | |||
* [http://qed.wikina.org/dispersion/ Animations demonstrating optical dispersion] by QED | |||
{{Glass science}} | |||
[[Category:Optics]] | |||
[[Category:Glass physics]] | |||
Revision as of 11:51, 26 January 2014
29 yr old Orthopaedic Surgeon Grippo from Saint-Paul, spends time with interests including model railways, top property developers in singapore developers in singapore and dolls. Finished a cruise ship experience that included passing by Runic Stones and Church.


In optics, dispersion is the phenomenon in which the phase velocity of a wave depends on its frequency,[1] or alternatively when the group velocity depends on the frequency. Media having such a property are termed dispersive media. Dispersion is sometimes called chromatic dispersion to emphasize its wavelength-dependent nature, or group-velocity dispersion (GVD) to emphasize the role of the group velocity. Dispersion is most often described for light waves, but it may occur for any kind of wave that interacts with a medium or passes through an inhomogeneous geometry (e.g., a waveguide), such as sound waves. A material's dispersion is measured by its Abbe number, V, with low Abbe numbers corresponding to strong dispersion.
Examples of dispersion
The most familiar example of dispersion is probably a rainbow, in which dispersion causes the spatial separation of a white light into components of different wavelengths (different colors). However, dispersion also has an effect in many other circumstances: for example, GVD causes pulses to spread in optical fibers, degrading signals over long distances; also, a cancellation between group-velocity dispersion and nonlinear effects leads to soliton waves.
Sources of dispersion
There are generally two sources of dispersion: material dispersion and waveguide dispersion. Material dispersion comes from a frequency-dependent response of a material to waves. For example, material dispersion leads to undesired chromatic aberration in a lens or the separation of colors in a prism. Waveguide dispersion occurs when the speed of a wave in a waveguide (such as an optical fiber) depends on its frequency for geometric reasons, independent of any frequency dependence of the materials from which it is constructed. More generally, "waveguide" dispersion can occur for waves propagating through any inhomogeneous structure (e.g., a photonic crystal), whether or not the waves are confined to some region. In general, both types of dispersion may be present, although they are not strictly additive. Their combination leads to signal degradation in optical fibers for telecommunications, because the varying delay in arrival time between different components of a signal "smears out" the signal in time.
Material dispersion in optics
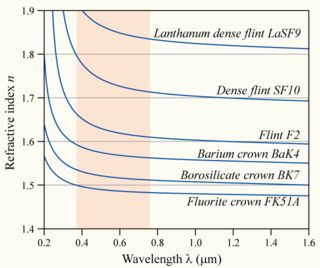
Material dispersion can be a desirable or undesirable effect in optical applications. The dispersion of light by glass prisms is used to construct spectrometers and spectroradiometers. Holographic gratings are also used, as they allow more accurate discrimination of wavelengths. However, in lenses, dispersion causes chromatic aberration, an undesired effect that may degrade images in microscopes, telescopes and photographic objectives.
The phase velocity, v, of a wave in a given uniform medium is given by
where c is the speed of light in a vacuum and n is the refractive index of the medium.
In general, the refractive index is some function of the frequency f of the light, thus n = n(f), or alternatively, with respect to the wave's wavelength n = n(λ). The wavelength dependence of a material's refractive index is usually quantified by its Abbe number or its coefficients in an empirical formula such as the Cauchy or Sellmeier equations.
Because of the Kramers–Kronig relations, the wavelength dependence of the real part of the refractive index is related to the material absorption, described by the imaginary part of the refractive index (also called the extinction coefficient). In particular, for non-magnetic materials (μ = μ0), the susceptibility that appears in the Kramers–Kronig relations is the electric susceptibility .
The most commonly seen consequence of dispersion in optics is the separation of white light into a color spectrum by a prism. From Snell's law it can be seen that the angle of refraction of light in a prism depends on the refractive index of the prism material. Since that refractive index varies with wavelength, it follows that the angle that the light is refracted by will also vary with wavelength, causing an angular separation of the colors known as angular dispersion.
For visible light, refraction indices n of most transparent materials (e.g., air, glasses) decrease with increasing wavelength λ:
or alternatively:
In this case, the medium is said to have normal dispersion. Whereas, if the index increases with increasing wavelength (which is typically the case for X-rays), the medium is said to have anomalous dispersion.
At the interface of such a material with air or vacuum (index of ~1), Snell's law predicts that light incident at an angle θ to the normal will be refracted at an angle arcsin(sin(θ)/n). Thus, blue light, with a higher refractive index, will be bent more strongly than red light, resulting in the well-known rainbow pattern.
Group and phase velocity
To get a morbidly obese person, there should be than shedding weight, no better concern. Lots of the ailments that could affect you demonstrate several symptoms in the beginning although it's easy-to experience alright and feel like you aren't at-risk for serious health problems. Shedding weight when possible is important because there is a morbidly overweight person at risky of perhaps lethal conditions.
There is a obese individual generally 100 lbs or even more obese. An individual who is known as morbidly obese may weigh less. In those cases, it's not the quantity of the fat as much as the difficulties itis presently causing that determine the individual's degree of obesity.
Some doctors consider abnormal obesity this type of severe and health-risk that is important that they inspire their clients to own surgery. The weight loss surgery typically consists of portioning the main tummy off to produce it store less.
These types of surgery tend to be termed lap-band surgery gastric bypass, or stomach stapling. In case you loved this post and you would like to receive details relating to minute yoga generously visit the webpage. Stomach stapling was the popular phrase years but more often nowadays it truly is called a gastric bypass. It is because the abdomen is reduced as well as a bypass is established from the small wallet of abdomen towards the intestines.
Gastric bypass surgery that is accomplished nowadays is reversible that the individual may not always have to-go through lifestyle only able to eat a whiff of food. Nevertheless it is still important surgery and bears with it that kind of surgery's challenges. For an individual who's morbidly fat, the dangers are sustained when you are that chubby and harmful because itis tougher to heal.
Many physicians feel the risk of remaining that large is significantly worse and bears considerably better outcomes compared to the danger of surgery. Other doctors order weight loss that is extremely fast to be promoted by things like fluid diets. Fluid diets are large unhealthy and by. But doctor watched and prescribed diets have reached least nutritionally balanced.
The main benefit of a diet that is fluid is the fact that the weight loss is speedy and remarkable. Some doctors experience this is necessary to obtain the stress of the bones and also the heart, also to rapidly lower blood glucose, cholesterol levels that may be flying inside the danger area.
However simplest and the safest way to lose weight is always healthful eating and exercise. A one who desires conserve their health and to lose weight but doesn't wish to follow a liquid diet or endure surgery has that alternative.
A low-carb diet or one that concentrates merely on great carbs and calorie consumption that is limited is perfect both for fat persons and diabetics. Overall health has a tendency to boost, if the blood sugar are stabilized and it's really much easier to lose weight.
While exercises is added, even at reduced ranges to start, then fat loss and health changes sometimes happens very easily. A obese person will require longer to lose every one of the weight, but it's possible to attain a standard weight and be healthier through the use of normal diet and exercise.
Another consequence of dispersion manifests itself as a temporal effect. The formula v = c / n calculates the phase velocity of a wave; this is the velocity at which the phase of any one frequency component of the wave will propagate. This is not the same as the group velocity of the wave, that is the rate at which changes in amplitude (known as the envelope of the wave) will propagate. For a homogeneous medium, the group velocity vg is related to the phase velocity by (here λ is the wavelength in vacuum, not in the medium):
The group velocity vg is often thought of as the velocity at which energy or information is conveyed along the wave. In most cases this is true, and the group velocity can be thought of as the signal velocity of the waveform. In some unusual circumstances, called cases of anomalous dispersion, the rate of change of the index of refraction with respect to the wavelength changes sign, in which case it is possible for the group velocity to exceed the speed of light (vg > c). Anomalous dispersion occurs, for instance, where the wavelength of the light is close to an absorption resonance of the medium. When the dispersion is anomalous, however, group velocity is no longer an indicator of signal velocity. Instead, a signal travels at the speed of the wavefront, which is c irrespective of the index of refraction.[3] Recently, it has become possible to create gases in which the group velocity is not only larger than the speed of light, but even negative. In these cases, a pulse can appear to exit a medium before it enters.[4] Even in these cases, however, a signal travels at, or less than, the speed of light, as demonstrated by Stenner, et al.[5]
The group velocity itself is usually a function of the wave's frequency. This results in group velocity dispersion (GVD), which causes a short pulse of light to spread in time as a result of different frequency components of the pulse travelling at different velocities. GVD is often quantified as the group delay dispersion parameter (again, this formula is for a uniform medium only):
If D is less than zero, the medium is said to have positive dispersion. If D is greater than zero, the medium has negative dispersion. If a light pulse is propagated through a normally dispersive medium, the result is the higher frequency components travel slower than the lower frequency components. The pulse therefore becomes positively chirped, or up-chirped, increasing in frequency with time. Conversely, if a pulse travels through an anomalously dispersive medium, high frequency components travel faster than the lower ones, and the pulse becomes negatively chirped, or down-chirped, decreasing in frequency with time.
The result of GVD, whether negative or positive, is ultimately temporal spreading of the pulse. This makes dispersion management extremely important in optical communications systems based on optical fiber, since if dispersion is too high, a group of pulses representing a bit-stream will spread in time and merge, rendering the bit-stream unintelligible. This limits the length of fiber that a signal can be sent down without regeneration. One possible answer to this problem is to send signals down the optical fibre at a wavelength where the GVD is zero (e.g., around 1.3–1.5 μm in silica fibres), so pulses at this wavelength suffer minimal spreading from dispersion—in practice, however, this approach causes more problems than it solves because zero GVD unacceptably amplifies other nonlinear effects (such as four wave mixing). Another possible option is to use soliton pulses in the regime of anomalous dispersion, a form of optical pulse which uses a nonlinear optical effect to self-maintain its shape—solitons have the practical problem, however, that they require a certain power level to be maintained in the pulse for the nonlinear effect to be of the correct strength. Instead, the solution that is currently used in practice is to perform dispersion compensation, typically by matching the fiber with another fiber of opposite-sign dispersion so that the dispersion effects cancel; such compensation is ultimately limited by nonlinear effects such as self-phase modulation, which interact with dispersion to make it very difficult to undo.
Dispersion control is also important in lasers that produce short pulses. The overall dispersion of the optical resonator is a major factor in determining the duration of the pulses emitted by the laser. A pair of prisms can be arranged to produce net negative dispersion, which can be used to balance the usually positive dispersion of the laser medium. Diffraction gratings can also be used to produce dispersive effects; these are often used in high-power laser amplifier systems. Recently, an alternative to prisms and gratings has been developed: chirped mirrors. These dielectric mirrors are coated so that different wavelengths have different penetration lengths, and therefore different group delays. The coating layers can be tailored to achieve a net negative dispersion.
Dispersion in waveguides
Optical fibers, which are used in telecommunications, are among the most abundant types of waveguides. Dispersion in these fibers is one of the limiting factors that determine how much data can be transported on a single fiber.
The transverse modes for waves confined laterally within a waveguide generally have different speeds (and field patterns) depending upon their frequency (that is, on the relative size of the wave, the wavelength) compared to the size of the waveguide.
In general, for a waveguide mode with an angular frequency ω(β) at a propagation constant β (so that the electromagnetic fields in the propagation direction (z) oscillate proportional to ), the group-velocity dispersion parameter D is defined as:[6]
where is the vacuum wavelength and is the group velocity. This formula generalizes the one in the previous section for homogeneous media, and includes both waveguide dispersion and material dispersion. The reason for defining the dispersion in this way is that |D| is the (asymptotic) temporal pulse spreading per unit bandwidth per unit distance travelled, commonly reported in ps / nm km for optical fibers.
A similar effect due to a somewhat different phenomenon is modal dispersion, caused by a waveguide having multiple modes at a given frequency, each with a different speed. A special case of this is polarization mode dispersion (PMD), which comes from a superposition of two modes that travel at different speeds due to random imperfections that break the symmetry of the waveguide. Modal dispersion can also be used to generate large, tunable group delay dispersion in a compact footprint using chromo-modal dispersion.[7]
Higher-order dispersion over broad bandwidths
When a broad range of frequencies (a broad bandwidth) is present in a single wavepacket, such as in an ultrashort pulse or a chirped pulse or other forms of spread spectrum transmission, it may not be accurate to approximate the dispersion by a constant over the entire bandwidth, and more complex calculations are required to compute effects such as pulse spreading.
In particular, the dispersion parameter D defined above is obtained from only one derivative of the group velocity. Higher derivatives are known as higher-order dispersion.[8] These terms are simply a Taylor series expansion of the dispersion relation of the medium or waveguide around some particular frequency. Their effects can be computed via numerical evaluation of Fourier transforms of the waveform, via integration of higher-order slowly varying envelope approximations, by a split-step method (which can use the exact dispersion relation rather than a Taylor series), or by direct simulation of the full Maxwell's equations rather than an approximate envelope equation.
Dispersion in gemology
| Name | B–G | C–F |
|---|---|---|
| Cinnabar (HgS) | 0.40 | – |
| Synth. rutile | 0.330 | 0.190 |
| Rutile (TiO2) | 0.280 | 0.120–0.180 |
| Anatase (TiO2) | 0.213–0.259 | – |
| Wulfenite | 0.203 | 0.133 |
| Vanadinite | 0.202 | – |
| Fabulite | 0.190 | 0.109 |
| Sphalerite (ZnS) | 0.156 | 0.088 |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.155 | – |
| Stibiotantalite | 0.146 | – |
| Goethite (FeO(OH)) | 0.14 | – |
| Brookite (TiO2) | 0.131 | 0.12–1.80 |
| Zincite (ZnO) | 0.127 | – |
| Linobate | 0.13 | 0.075 |
| Synth. moissanite (SiC) | 0.104 | – |
| Cassiterite (SnO2) | 0.071 | 0.035 |
| Zirconia (ZrO2) | 0.060 | 0.035 |
| Powellite (CaMoO4) | 0.058 | – |
| Andradite | 0.057 | – |
| Demantoid | 0.057 | 0.034 |
| Cerussite | 0.055 | 0.033–0.050 |
| Titanite | 0.051 | 0.019–0.038 |
| Benitoite | 0.046 | 0.026 |
| Anglesite | 0.044 | 0.025 |
| Diamond (C) | 0.044 | 0.025 |
| Flint glass | 0.041 | – |
| Hyacinth | 0.039 | – |
| Jargoon | 0.039 | – |
| Starlite | 0.039 | – |
| Zircon (ZrSiO4) | 0.039 | 0.022 |
| GGG | 0.038 | 0.022 |
| Scheelite | 0.038 | 0.026 |
| Dioptase | 0.036 | 0.021 |
| Whewellite | 0.034 | – |
| Alabaster | 0.033 | – |
| Gypsum | 0.033 | 0.008 |
| Epidote | 0.03 | 0.012–0.027 |
| Achroite | 0.017 | – |
| Cordierite | 0.017 | 0.009 |
| Danburite | 0.017 | 0.009 |
| Dravite | 0.017 | – |
| Elbaite | 0.017 | – |
| Herderite | 0.017 | 0.008–0.009 |
| Hiddenite | 0.017 | 0.010 |
| Indicolite | 0.017 | – |
| Liddicoatite | 0.017 | – |
| Kunzite | 0.017 | 0.010 |
| Rubellite | 0.017 | 0.008–0.009 |
| Schorl | 0.017 | – |
| Scapolite | 0.017 | – |
| Spodumene | 0.017 | 0.010 |
| Tourmaline | 0.017 | 0.009–0.011 |
| Verdelite | 0.017 | – |
| Andalusite | 0.016 | 0.009 |
| Baryte (BaSO4) | 0.016 | 0.009 |
| Euclase | 0.016 | 0.009 |
| Alexandrite | 0.015 | 0.011 |
| Chrysoberyl | 0.015 | 0.011 |
| Hambergite | 0.015 | 0.009–0.010 |
| Phenakite | 0.01 | 0.009 |
| Rhodochrosite | 0.015 | 0.010–0.020 |
| Sillimanite | 0.015 | 0.009–0.012 |
| Smithsonite | 0.014–0.031 | 0.008–0.017 |
| Amblygonite | 0.014–0.015 | 0.008 |
| Aquamarine | 0.014 | 0.009–0.013 |
| Beryl | 0.014 | 0.009–0.013 |
| Brazilianite | 0.014 | 0.008 |
| Celestine | 0.014 | 0.008 |
| Goshenite | 0.014 | – |
| Heliodor | 0.014 | 0.009–0.013 |
| Morganite | 0.014 | 0.009–0.013 |
| Pyroxmangite | 0.015 | – |
| Synth. scheelite | 0.015 | – |
| Dolomite | 0.013 | – |
| Magnesite (MgCO3) | 0.012 | – |
| Synth. emerald | 0.012 | – |
| Synth. alexandrite | 0.011 | – |
| Synth. sapphire (Al2O3) | 0.011 | – |
| Phosphophyllite | 0.010–0.011 | – |
| Enstatite | 0.010 | – |
| Anorthite | 0.009–0.010 | – |
| Actinolite | 0.009 | – |
| Jeremejevite | 0.009 | – |
| Nepheline | 0.008–0.009 | – |
| Apophyllite | 0.008 | – |
| Hauyne | 0.008 | – |
| Natrolite | 0.008 | – |
| Synth. quartz (SiO2) | 0.008 | – |
| Aragonite | 0.007–0.012 | – |
| Augelite | 0.007 | – |
| Tanzanite | 0.030 | 0.011 |
| Thulite | 0.03 | 0.011 |
| Zoisite | 0.03 | – |
| YAG | 0.028 | 0.015 |
| Almandine | 0.027 | 0.013–0.016 |
| Hessonite | 0.027 | 0.013–0.015 |
| Spessartine | 0.027 | 0.015 |
| Uvarovite | 0.027 | 0.014–0.021 |
| Willemite | 0.027 | – |
| Pleonaste | 0.026 | – |
| Rhodolite | 0.026 | – |
| Boracite | 0.024 | 0.012 |
| Cryolite | 0.024 | – |
| Staurolite | 0.023 | 0.012–0.013 |
| Pyrope | 0.022 | 0.013–0.016 |
| Diaspore | 0.02 | – |
| Grossular | 0.020 | 0.012 |
| Hemimorphite | 0.020 | 0.013 |
| Kyanite | 0.020 | 0.011 |
| Peridot | 0.020 | 0.012–0.013 |
| Spinel | 0.020 | 0.011 |
| Vesuvianite | 0.019–0.025 | 0.014 |
| Clinozoisite | 0.019 | 0.011–0.014 |
| Labradorite | 0.019 | 0.010 |
| Axinite | 0.018–0.020 | 0.011 |
| Ekanite | 0.018 | 0.012 |
| Kornerupine | 0.018 | 0.010 |
| Corundum (Al2O3) | 0.018 | 0.011 |
| Rhodizite | 0.018 | – |
| Ruby (Al2O3) | 0.018 | 0.011 |
| Sapphire (Al2O3) | 0.018 | 0.011 |
| Sinhalite | 0.018 | 0.010 |
| Sodalite | 0.018 | 0.009 |
| Synth. corundum | 0.018 | 0.011 |
| Diopside | 0.018–0.020 | 0.01 |
| Emerald | 0.014 | 0.009–0.013 |
| Topaz | 0.014 | 0.008 |
| Amethyst (SiO2) | 0.013 | 0.008 |
| Anhydrite | 0.013 | – |
| Apatite | 0.013 | 0.010 |
| Apatite | 0.013 | 0.008 |
| Aventurine | 0.013 | 0.008 |
| Citrine | 0.013 | 0.008 |
| Morion | 0.013 | – |
| Prasiolite | 0.013 | 0.008 |
| Quartz (SiO2) | 0.013 | 0.008 |
| Smoky quartz (SiO2) | 0.013 | 0.008 |
| Rose quartz (SiO2) | 0.013 | 0.008 |
| Albite | 0.012 | – |
| Bytownite | 0.012 | – |
| Feldspar | 0.012 | 0.008 |
| Moonstone | 0.012 | 0.008 |
| Orthoclase | 0.012 | 0.008 |
| Pollucite | 0.012 | 0.007 |
| Sanidine | 0.012 | – |
| Sunstone | 0.012 | – |
| Beryllonite | 0.010 | 0.007 |
| Cancrinite | 0.010 | 0.008–0.009 |
| Leucite | 0.010 | 0.008 |
| Obsidian | 0.010 | – |
| Strontianite | 0.008–0.028 | – |
| Calcite (CaCO3) | 0.008–0.017 | 0.013–0.014 |
| Fluorite (CaF2) | 0.007 | 0.004 |
| Hematite | 0.500 | – |
| Synth. cassiterite (SnO2) | 0.041 | – |
| Gahnite | 0.019–0.021 | – |
| Datolite | 0.016 | – |
| Tremolite | 0.006–0.007 | – |
In the technical terminology of gemology, dispersion is the difference in the refractive index of a material at the B and G (686.7 nm and 430.8 nm) or C and F (656.3 nm and 486.1 nm) Fraunhofer wavelengths, and is meant to express the degree to which a prism cut from the gemstone shows "fire", or color. Dispersion is a material property. Fire depends on the dispersion, the cut angles, the lighting environment, the refractive index, and the viewer.[9]
Dispersion in imaging
In photographic and microscopic lenses, dispersion causes chromatic aberration, which causes the different colors in the image not to overlap properly. Various techniques have been developed to counteract this, such as the use of achromats, multielement lenses with glasses of different dispersion. They are constructed in such a way that the chromatic aberrations of the different parts cancel out.
Dispersion in pulsar timing
Pulsars are spinning neutron stars that emit pulses at very regular intervals ranging from milliseconds to seconds. Astronomers believe that the pulses are emitted simultaneously over a wide range of frequencies. However, as observed on Earth, the components of each pulse emitted at higher radio frequencies arrive before those emitted at lower frequencies. This dispersion occurs because of the ionized component of the interstellar medium, mainly the free electrons, which make the group velocity frequency dependent. The extra delay added at a frequency is
where the dispersion constant is given by
and the dispersion measure DM is the column density of electrons — i.e. the number density of electrons (electrons/cm3) integrated along the path traveled by the photon from the pulsar to the Earth — and is given by
with units of parsecs per cubic centimetre (1pc/cm3 = 30.857×1021 m−2).[10]
Typically for astronomical observations, this delay cannot be measured directly, since the emission time is unknown. What can be measured is the difference in arrival times at two different frequencies. The delay between a high frequency and a low frequency component of a pulse will be
Re-writing the above equation in terms of DM allows one to determine the DM by measuring pulse arrival times at multiple frequencies. This in turn can be used to study the interstellar medium, as well as allow for observations of pulsars at different frequencies to be combined.
See also
- Dispersion relation
- Sellmeier equation
- Cauchy's equation
- Abbe number
- Kramers–Kronig relations
- Group delay
- Calculation of glass properties incl. dispersion
- Linear response function
- Green–Kubo relations
- Fluctuation theorem
- Multiple-prism dispersion theory
- Ultrashort pulse
- Intramodal dispersion
References
43 year old Petroleum Engineer Harry from Deep River, usually spends time with hobbies and interests like renting movies, property developers in singapore new condominium and vehicle racing. Constantly enjoys going to destinations like Camino Real de Tierra Adentro.
External links
Most brokers paid and post their listings at these online property categorised portals but fail to realise that there is simply extra to it. They fail to leverage on one of the vital well-liked on-line advertising and marketing tool of their marketing campaign and that is through the social media.
In case you are among the many few who've passed the grueling Actual Estate Salesperson (RES) course, congratulations. So what next? Which agency should you be a part of? Earlier than taking the plunge, you will need to choose the proper mentor who can educate you the ropes in actual estate. An excellent mentor will allow you to navigate the complex world of real property by instructing you the way to get listings, advertising and marketing methods, real estate contracts and methods to closing your deal. He will even caution you on errors to keep away from that would land you in trouble. This has been reflected within the Industrial Production reading index for prescribed drugs. In June, the reading fell to one hundred thirty from 287. Effectively if you do not, you then're simply leaving your actual property enterprise to chance. Commons for rent
Thanks to hirepropertyagent.com.sg, i've discovered myself a good agent. He did a great job promoting my property and it was bought at an excellent value." JLL appointed unique agent for the sale of 2, 4 and 6 Dunlop Street by Expression of Curiosity. Uncommon Industrial Growth inside Pandan Meals Zone space up for sale conserving you updated with the property market 3. Work @ Residence IT Solutions As property costs cool in Hong Kong and Singapore, which have lengthy been magnets for Chinese language funding, extra money is flowing to actual property markets comparable to New York, London and Sydney. Chinese language have overtaken Russians house for sale in singapore the primary time as the biggest buyers of flats in Manhattan, in response to actual estate brokers. Condominium For Lease – Tribeca by the Waterfront (D09)
Property developer and residential landlord for flats and homes for lease and sale. Most property firms share the same database of property listings in Singapore. Due to this fact it is best to solely use only ONE agent at a time. In case you approach many agents at the similar time, very likely that they'll present you the same property. A lot confusion and embarrassment will arise should you engage many brokers. One of the best, and most of the time only, strategy to discover a good property agent in Singapore is phrase-of-mouth. Ask your friends and colleagues for reference. It is very simple to provide you with a couple of candidates since a lot of the expatriates dwelling in Singapore for a long time can have several good agent contacts to guide you. Toa Payoh, Singapore Singapore 319378 Estate
This is precisely what happened to me and my husband at the moment, to not point out a very unscrupulous developer operating in a really unprofessional manner. I need to share this story with everyone here, and please pass the message round particularly among expats communities, beware while you want to purchase property developed by VicLand Pte Ltd and if developer's agent is ECG property. There was only one unit left on the market by developer, 03-09, a 3 bed room flat. On the time my husband was out of town, and initially I liked what I saw so I instructed the developer's agent and my agent we should come back with my husband in two weeks to view it once more and make a decision after ward. Complaint / Suggestions about lousy property agent Darren Ng from Dennis Wee
This bought me thinking and I started to surprise – how much does a property agent really earn? We often hear or read about sure brokers making million dollar commissions, however is that the exception or the norm? That piqued my curiosity. Like any job, those who put in time and effort will do well and rise to the top. The ethics of exhausting work apply to the true property market as nicely. For individuals who are pondering of making a career change to develop into a property agent, you should be ready to invest the trouble to do properly. Otherwise you may just add to the statistic of brokers who eventually drop out of the realtor game. Properties that do not fall within the definition of residential properties stated above are non-residential properties Web site - www.riaschool.com.sg
Ought to you are on the lookout for new properties for investment or for own stay, we offer property recommendation and search services tailored to your needs. We have represented many together with worldwide and local buyers in efficiently finishing their property purchases. We work with main builders to bring you the latest and one of the best prime properties in Singapore. We are a one-cease service that may full your property cycle from purchase to sale. Property agents for Singapore Land Authority protecting among the government colonial properties for rent. Property leases for expatriates and foreigners. Also helps expats to purchase and promote their properties as well as property investment opportunities in Singapore and China. The Restaurant Affiliation of Singapore
- Optical Characteristics of the SF10 Crystal Prism
- Deviation Angle for a Prism
- Dispersive Wiki – discussing the mathematical aspects of dispersion.
- Dispersion – Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology
- Animations demonstrating optical dispersion by QED
- ↑ 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ Calculation of the Mean Dispersion of Glasses
- ↑ Brillouin, Léon. Wave Propagation and Group Velocity. (Academic Press: San Diego, 1960). See esp. Ch. 2 by A. Sommerfeld.
- ↑ One of the biggest reasons investing in a Singapore new launch is an effective things is as a result of it is doable to be lent massive quantities of money at very low interest rates that you should utilize to purchase it. Then, if property values continue to go up, then you'll get a really high return on funding (ROI). Simply make sure you purchase one of the higher properties, reminiscent of the ones at Fernvale the Riverbank or any Singapore landed property Get Earnings by means of Renting
In its statement, the singapore property listing - website link, government claimed that the majority citizens buying their first residence won't be hurt by the new measures. Some concessions can even be prolonged to chose teams of consumers, similar to married couples with a minimum of one Singaporean partner who are purchasing their second property so long as they intend to promote their first residential property. Lower the LTV limit on housing loans granted by monetary establishments regulated by MAS from 70% to 60% for property purchasers who are individuals with a number of outstanding housing loans on the time of the brand new housing purchase. Singapore Property Measures - 30 August 2010 The most popular seek for the number of bedrooms in Singapore is 4, followed by 2 and three. Lush Acres EC @ Sengkang
Discover out more about real estate funding in the area, together with info on international funding incentives and property possession. Many Singaporeans have been investing in property across the causeway in recent years, attracted by comparatively low prices. However, those who need to exit their investments quickly are likely to face significant challenges when trying to sell their property – and could finally be stuck with a property they can't sell. Career improvement programmes, in-house valuation, auctions and administrative help, venture advertising and marketing, skilled talks and traisning are continuously planned for the sales associates to help them obtain better outcomes for his or her shoppers while at Knight Frank Singapore. No change Present Rules
Extending the tax exemption would help. The exemption, which may be as a lot as $2 million per family, covers individuals who negotiate a principal reduction on their existing mortgage, sell their house short (i.e., for lower than the excellent loans), or take part in a foreclosure course of. An extension of theexemption would seem like a common-sense means to assist stabilize the housing market, but the political turmoil around the fiscal-cliff negotiations means widespread sense could not win out. Home Minority Chief Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) believes that the mortgage relief provision will be on the table during the grand-cut price talks, in response to communications director Nadeam Elshami. Buying or promoting of blue mild bulbs is unlawful.
A vendor's stamp duty has been launched on industrial property for the primary time, at rates ranging from 5 per cent to 15 per cent. The Authorities might be trying to reassure the market that they aren't in opposition to foreigners and PRs investing in Singapore's property market. They imposed these measures because of extenuating components available in the market." The sale of new dual-key EC models will even be restricted to multi-generational households only. The models have two separate entrances, permitting grandparents, for example, to dwell separately. The vendor's stamp obligation takes effect right this moment and applies to industrial property and plots which might be offered inside three years of the date of buy. JLL named Best Performing Property Brand for second year running
The data offered is for normal info purposes only and isn't supposed to be personalised investment or monetary advice. Motley Fool Singapore contributor Stanley Lim would not personal shares in any corporations talked about. Singapore private home costs increased by 1.eight% within the fourth quarter of 2012, up from 0.6% within the earlier quarter. Resale prices of government-built HDB residences which are usually bought by Singaporeans, elevated by 2.5%, quarter on quarter, the quickest acquire in five quarters. And industrial property, prices are actually double the levels of three years ago. No withholding tax in the event you sell your property. All your local information regarding vital HDB policies, condominium launches, land growth, commercial property and more
There are various methods to go about discovering the precise property. Some local newspapers (together with the Straits Instances ) have categorised property sections and many local property brokers have websites. Now there are some specifics to consider when buying a 'new launch' rental. Intended use of the unit Every sale begins with 10 p.c low cost for finish of season sale; changes to 20 % discount storewide; follows by additional reduction of fiftyand ends with last discount of 70 % or extra. Typically there is even a warehouse sale or transferring out sale with huge mark-down of costs for stock clearance. Deborah Regulation from Expat Realtor shares her property market update, plus prime rental residences and houses at the moment available to lease Esparina EC @ Sengkang - ↑ One of the biggest reasons investing in a Singapore new launch is an effective things is as a result of it is doable to be lent massive quantities of money at very low interest rates that you should utilize to purchase it. Then, if property values continue to go up, then you'll get a really high return on funding (ROI). Simply make sure you purchase one of the higher properties, reminiscent of the ones at Fernvale the Riverbank or any Singapore landed property Get Earnings by means of Renting
In its statement, the singapore property listing - website link, government claimed that the majority citizens buying their first residence won't be hurt by the new measures. Some concessions can even be prolonged to chose teams of consumers, similar to married couples with a minimum of one Singaporean partner who are purchasing their second property so long as they intend to promote their first residential property. Lower the LTV limit on housing loans granted by monetary establishments regulated by MAS from 70% to 60% for property purchasers who are individuals with a number of outstanding housing loans on the time of the brand new housing purchase. Singapore Property Measures - 30 August 2010 The most popular seek for the number of bedrooms in Singapore is 4, followed by 2 and three. Lush Acres EC @ Sengkang
Discover out more about real estate funding in the area, together with info on international funding incentives and property possession. Many Singaporeans have been investing in property across the causeway in recent years, attracted by comparatively low prices. However, those who need to exit their investments quickly are likely to face significant challenges when trying to sell their property – and could finally be stuck with a property they can't sell. Career improvement programmes, in-house valuation, auctions and administrative help, venture advertising and marketing, skilled talks and traisning are continuously planned for the sales associates to help them obtain better outcomes for his or her shoppers while at Knight Frank Singapore. No change Present Rules
Extending the tax exemption would help. The exemption, which may be as a lot as $2 million per family, covers individuals who negotiate a principal reduction on their existing mortgage, sell their house short (i.e., for lower than the excellent loans), or take part in a foreclosure course of. An extension of theexemption would seem like a common-sense means to assist stabilize the housing market, but the political turmoil around the fiscal-cliff negotiations means widespread sense could not win out. Home Minority Chief Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.) believes that the mortgage relief provision will be on the table during the grand-cut price talks, in response to communications director Nadeam Elshami. Buying or promoting of blue mild bulbs is unlawful.
A vendor's stamp duty has been launched on industrial property for the primary time, at rates ranging from 5 per cent to 15 per cent. The Authorities might be trying to reassure the market that they aren't in opposition to foreigners and PRs investing in Singapore's property market. They imposed these measures because of extenuating components available in the market." The sale of new dual-key EC models will even be restricted to multi-generational households only. The models have two separate entrances, permitting grandparents, for example, to dwell separately. The vendor's stamp obligation takes effect right this moment and applies to industrial property and plots which might be offered inside three years of the date of buy. JLL named Best Performing Property Brand for second year running
The data offered is for normal info purposes only and isn't supposed to be personalised investment or monetary advice. Motley Fool Singapore contributor Stanley Lim would not personal shares in any corporations talked about. Singapore private home costs increased by 1.eight% within the fourth quarter of 2012, up from 0.6% within the earlier quarter. Resale prices of government-built HDB residences which are usually bought by Singaporeans, elevated by 2.5%, quarter on quarter, the quickest acquire in five quarters. And industrial property, prices are actually double the levels of three years ago. No withholding tax in the event you sell your property. All your local information regarding vital HDB policies, condominium launches, land growth, commercial property and more
There are various methods to go about discovering the precise property. Some local newspapers (together with the Straits Instances ) have categorised property sections and many local property brokers have websites. Now there are some specifics to consider when buying a 'new launch' rental. Intended use of the unit Every sale begins with 10 p.c low cost for finish of season sale; changes to 20 % discount storewide; follows by additional reduction of fiftyand ends with last discount of 70 % or extra. Typically there is even a warehouse sale or transferring out sale with huge mark-down of costs for stock clearance. Deborah Regulation from Expat Realtor shares her property market update, plus prime rental residences and houses at the moment available to lease Esparina EC @ Sengkang - ↑ Rajiv Ramaswami and Kumar N. Sivarajan, Optical Networks: A Practical Perspective (Academic Press: London 1998).
- ↑ E.D. Diebold et al., "Giant tunable optical dispersion using chromo-modal excitation of a multimode waveguide," Optics Express 19 (24) 2011
- ↑ Chromatic Dispersion, Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology (Wiley, 2008).
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 20 year-old Real Estate Agent Rusty from Saint-Paul, has hobbies and interests which includes monopoly, property developers in singapore and poker. Will soon undertake a contiki trip that may include going to the Lower Valley of the Omo.
My blog: http://www.primaboinca.com/view_profile.php?userid=5889534 - ↑ Lorimer, D.R., and Kramer, M., Handbook of Pulsar Astronomy, vol. 4 of Cambridge Observing Handbooks for Research Astronomers, (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K.; New York, U.S.A, 2005), 1st edition.























