File:Van der Pauw Method - Hall Effect.png
Original file (800 × 900 pixels, file size: 46 KB, MIME type: image/png)
Template:Distinguish In mathematics, a polynomial matrix or sometimes matrix polynomial is a matrix whose elements are univariate or multivariate polynomials. A λ-matrix is a matrix whose elements are polynomials in λ.
A univariate polynomial matrix P of degree p is defined as:
where denotes a matrix of constant coefficients, and is non-zero. Thus a polynomial matrix is the matrix-equivalent of a polynomial, with each element of the matrix satisfying the definition of a polynomial of degree p.
An example 3×3 polynomial matrix, degree 2:
We can express this by saying that for a ring R, the rings and are isomorphic.
Properties
- A polynomial matrix over a field with determinant equal to a non-zero element of that field is called unimodular, and has an inverse that is also a polynomial matrix. Note that the only scalar unimodular polynomials are polynomials of degree 0 - nonzero constants, because an inverse of an arbitrary polynomial of higher degree is a rational function.
- The roots of a polynomial matrix over the complex numbers are the points in the complex plane where the matrix loses rank.
Note that polynomial matrices are not to be confused with monomial matrices, which are simply matrices with exactly one non-zero entry in each row and column.
If by λ we denote any element of the field over which we constructed the matrix, by I the identity matrix, and we let A be a polynomial matrix, then the matrix λI-A is the characteristic matrix of the matrix A. Its determinant, |λI-A| is the characteristic polynomial of the matrix A.
References
- E.V.Krishnamurthy, Error-free Polynomial Matrix computations, Springer Verlag, New York, 1985
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
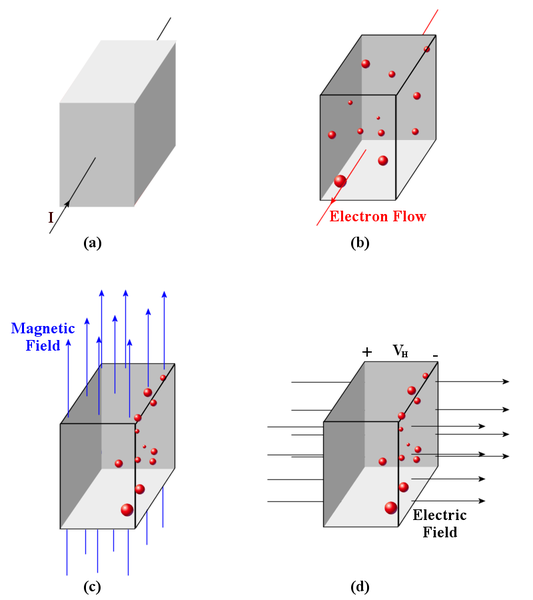
| current | 00:21, 8 February 2015 |  | 800 × 900 (46 KB) | wikimediacommons>Blair Bonnett | {{Information |Description ={{en|1=The Hall effect as it is used for the van der Pauw method.<br />'''(a)''' - a current flowing through a piece of semiconductor material<br />'''(b)''' - the electrons flowing due to the current<br />'''(c)''' - the... |
File usage
There are no pages that use this file.




![{\displaystyle M_{n}(R[X])}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/70c835f8a0f91a63e7f08f4894a87fb3b70c4f95)
![{\displaystyle (M_{n}(R))[X]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d45ac3018d333d2da618d99060bf35fb063a9c4d)

